Breakthrough Study Reveals Key Link Between CTI and Liver Health: A Game Changer for NAFLD and Fibrosis
2025-04-12
Author: Mei
Unlocking the Mystery of Liver Disease: Groundbreaking Research Takes Center Stage
In a stunning revelation that could reshape our approach to liver health, a recent study has highlighted a powerful correlation between the high-sensitivity C-reactive protein-triglyceride glucose index (CTI) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), along with liver fibrosis. With NAFLD affecting a staggering 25% of the global population, this research promises to unveil critical insights about its underlying mechanisms.
Study Details: What the Researchers Did
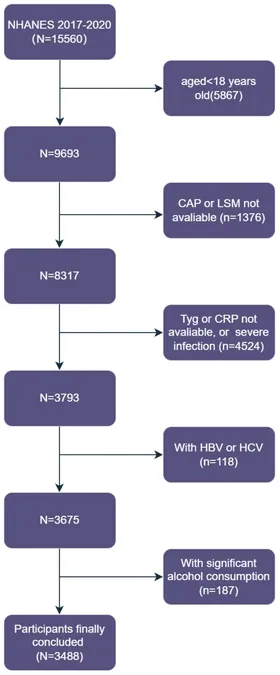
Conducted using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) spanning 2017 to 2020, this cross-sectional study analyzed the health profiles of 3,488 American adults. By determining CTI through a novel formula that integrates both insulin resistance and inflammatory markers, researchers set the stage to explore its connection to liver conditions.
Shocking Findings: CTI’s Role Revealed
The results were compelling. A remarkable 42.7% of participants were diagnosed with NAFLD, and 9.4% exhibited liver fibrosis. As the CTI levels rose, so did the likelihood of these conditions—showing a striking positive correlation. Even after adjusting for potential confounders, the odds of having NAFLD went up by 94% and liver fibrosis by 38% with elevated CTI levels.
CTI Outshines Other Markers: A New Era in Diagnostics?
The research revealed that CTI outperformed traditional diagnostic markers, like the triglyceride glucose index (TyG) and hs-CRP, when it came to identifying NAFLD and liver fibrosis. With an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.756 for NAFLD and 0.702 for liver fibrosis, CTI stands out as a potentially vital tool for clinicians.
Understanding NAFLD: A Growing Public Health Concern
NAFLD is not just a liver condition; it's a major public health issue linked to severe metabolic disorders and increased risks of serious diseases, including cardiovascular problems and certain cancers. As it progresses from simple fatty liver to severe liver fibrosis, the consequences become dire, highlighting the urgent need for effective screening and management.
Why This Study Matters: Implications for Future Research
This groundbreaking study paves the way for further exploration of CTI as a composite index—a reliable predictor of both insulin resistance and inflammation. It fosters a deeper understanding of NAFLD’s complexities and empowers healthcare professionals to better target interventions that combat this prolific disease.
Strengths and Limitations: A Balanced Perspective
While this research boasts significant strengths—including large sample size and innovative methodology—it also acknowledges the limitations inherent in cross-sectional studies, such as the inability to definitively establish causal relationships. Future prospective studies are crucial to validate these promising findings.
The Path Ahead: A Call for Proactive Liver Health Monitoring
As the world grapples with rising rates of liver disease, the findings champion a proactive approach, urging the need for routine assessments of CTI alongside lifestyle modifications to mitigate risks. With further research on CTI's implications for metabolic health on the horizon, this study could very well mark the beginning of a new chapter in liver disease prevention and treatment.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)