
Chinese Astronauts Showcase Flame Behavior in Weightlessness on Tiangong Space Station
2024-10-03
Author: Wei Ling
Introduction
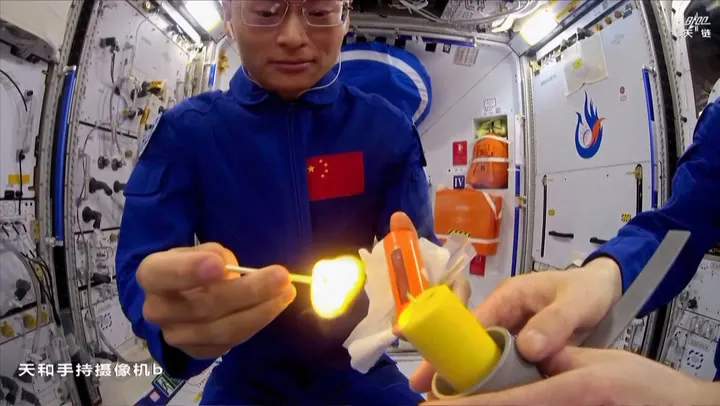
In a fascinating demonstration of science, Chinese astronauts aboard the Tiangong Space Station recently conducted an experiment to light a candle with a match, providing valuable insights into how flames behave in microgravity. This experiment is part of ongoing research to understand combustion in space, which has significant implications for safety and life support in long-duration missions.
Flame Behavior in Microgravity
Unlike on Earth, where gravity pulls hot gases upward, creating a distinct flame shape, the flames in space behave quite differently. They tend to form spherical shapes due to the lack of gravitational forces, which can have profound implications for future space exploration, including the optimization of combustion engines and the development of safe habitats for astronauts.
Importance of the Experiment
The significance of such experiments cannot be understated, as they help scientists understand how fire reacts in environments devoid of the familiar forces we experience on our planet. NASA and other space agencies have previously engaged in similar research to improve safety protocols and technological advancements in spacecraft.
China's Role in Space Exploration
This groundbreaking work on the Tiangong Space Station also highlights China's growing capabilities in space exploration and its commitment to advancing human knowledge. As international collaboration in space science continues, findings from such experiments will contribute to a broader understanding of physics and engineering that can ultimately benefit life on Earth as well.
Conclusion
In a world where space exploration is becoming increasingly pivotal, the Tiangong Space Station serves as a beacon of discovery. What’s next for the Chinese space program? As they push the boundaries of scientific understanding, the future looks bright for astronauts and researchers alike!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)