Discovering Life on Icy Moons: The Revolutionary Exo-AUV Strategy
2025-01-04
Author: Jia
Sydney, Australia (SPX) – As the quest for extraterrestrial life intensifies, icy moons like Europa and Enceladus are emerging as key battlegrounds in this cosmic exploration. These frozen worlds hold immense promise for uncovering potential biosignatures and prebiotic chemical systems concentrated in their icy shells, interfaces, and ocean floors. A groundbreaking approach utilizing Extraterrestrial Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (Exo-AUVs) is set to transform our understanding of these enigmatic environments.
The Promise of Europa and Enceladus
Europa, with its thick ice crust covering an ocean that could harbor life, presents a compelling case for exploration. Researchers are shifting away from traditional binary methods of detection, which categorically classify findings as either life or non-life. Instead, the focus is on understanding the intricate ecological variables that govern these alien worlds, allowing for the identification of high-potential regions for life.
A Strategic Approach to Life Detection
The detection of life is not a simple endeavor; it requires a strategic plan composed of four critical steps: assuming, sampling, analyzing, and verifying. By employing ecological niche theory, Exo-AUVs can be directed to micro-zones teeming with potential biosignatures, paving the way for the discovery of existing life forms or prebiotic conditions. Their advanced technology enables data collection that can be leveraged to enhance our Earth-based models of life.
The Role of Exo-AUVs
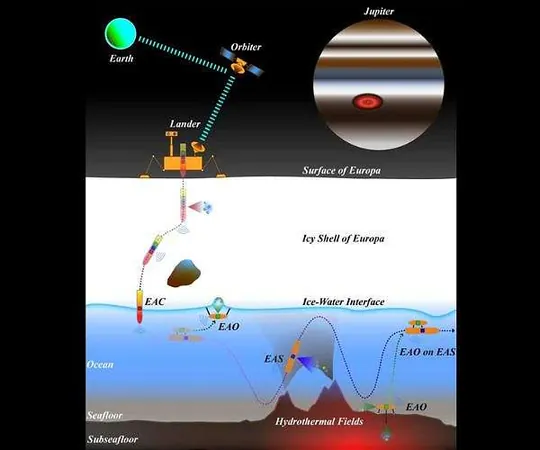
But what makes Exo-AUVs indispensable in this icy frontier? Equipped to operate in extreme conditions, they utilize innovative ice-penetrating carriers powered by Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) or Radioisotope Thermal Generators (RTGs). These carriers not only transport Exo-AUVs but also act as mobile bases, facilitating data transfer and recharging in the harsh environments of Europa.
Challenges of Deep Space Exploration
Despite their promise, significant hurdles remain. The vast distance from Earth introduces communication delays of up to half an hour, necessitating high levels of autonomy in Exo-AUV operations. These vehicles must independently navigate and execute scientific tasks, assessing potential biological regions and dynamically adjusting their strategies based on real-time analysis.
The Multi-Exo-AUV System (MEAS)
A cutting-edge concept known as the Multi-Exo-AUV System (MEAS) is at the forefront of this exploration strategy. This system comprises an ice-penetrating carrier supported by specialized Exo-AUVs designed for extensive surveying and precise observation. Such a system maximizes efficiency and enhances adaptability to the unforgiving conditions found beneath Europa's icy surface.
Collaborative Detection Networks
Moreover, the development of Exo-AUVs in both the U.S. and Europe points to the pressing need for tailored solutions that specifically tackle the complex life detection challenges on these icy worlds. A comprehensive roadmap is being devised to align scientific aspirations with the technological advancements necessary to conquer Europa's unique operational obstacles.
Looking to the Future
Perhaps most significantly, the MEAS approach fosters the establishment of a collaborative detection network—a foundational strategy for comprehensive exploration across Europa's vast ice and ocean systems. By overcoming the limitations inherent in current design frameworks, this bold strategy holds the potential to significantly advance our extraterrestrial life search efforts.
As we stand on the brink of potentially groundbreaking discoveries, the future of life detection on icy moons looks brighter than ever. Could we soon uncover evidence that changes everything we know about life beyond Earth? Stay tuned!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)