
Disturbing New Discovery Shakes Understanding of Zika Virus and Pregnancy: What You Need to Know!
2025-03-23
Author: Yu
Groundbreaking Study Reveals Zika Virus Mechanism
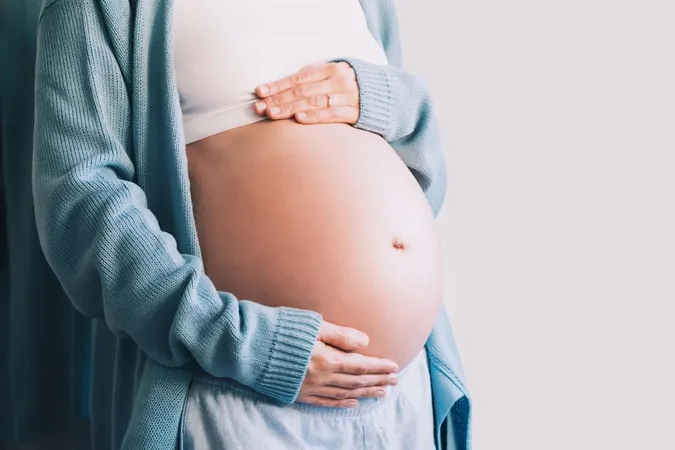
In a groundbreaking study, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have unveiled a troubling mechanism by which the Zika virus infiltrates the placentas of pregnant women, posing serious risks to fetal health.
So, what exactly is happening?
The team has identified that the Zika virus employs an ingenious tactic, creating tiny channels known as nanotubes within the placental cells. These nanotubes allow the virus to stealthily bypass the placental barrier—a critical defense that normally shields the fetus from harmful microbes and chemicals. This revelation underscores a key vulnerability in the protective mechanisms of pregnant women.
Published Findings
Published in the prestigious journal *Nature Communications*, the study highlights that this nanotube formation occurs with minimal activation of the immune system, which would typically react to such intrusions. Rafael T. Michita, the lead author of the study, emphasized the significance of the Zika protein NS1 in this process: "Exposure of placental cells to the NS1 protein triggers tunnel formation, paving the way for the virus to invade neighboring cells."
Pivotal Importance of the Research
Notably, while other viruses—such as HIV, herpes, and the flu—can induce similar channels in host cells, this is the first instance where such tunneling has been explicitly linked to Zika virus infection in placental cells.
Why is this research pivotal?
These alarming findings could pave the way for the development of targeted therapeutic strategies to combat this stealthy transmission. Co-senior author Indira Mysorekar stated, "We offer vital insights that could lead to innovative preventive measures against this mode of transmission."
Implications of Zika Virus Infection
The implications of Zika virus infection during pregnancy are dire, often resulting in severe neurological disorders, congenital abnormalities, or even fetal death. Currently, there are no vaccines or specific antiviral treatments available, raising concern amidst the ongoing public health challenges.
The Bigger Picture: Climate Change and Expanding Zika Risks
As if this isn't concerning enough, the ongoing climate crisis is expected to exacerbate the situation. Rising global temperatures may extend the habitats of the mosquitoes that transmit Zika and other dangerous vector-borne diseases like dengue and malaria. Reports indicate that warmer climates in Europe have already pushed these disease-carrying vectors further north and to higher altitudes, with similar trends observed in regions like the Ethiopian Highlands.
Future Risks of Mosquito Populations
Researchers are also warning that as temperatures continue to rise, we can expect an increase in the populations of various mosquito species across North and South America. This changing landscape could pose unprecedented public health challenges.
Innovative Approaches to Combat Vector-Borne Diseases
Globally, steps are being taken to mitigate the threat posed by mosquitoes. In Florida, one innovative initiative involves using X-rays to eliminate invasive mosquito populations that spread diseases. At the same time, a collaborative research endeavor between scientists from the U.S. and Burkina Faso is exploring a novel approach that harnesses genetically engineered fungi to control malaria-carrying mosquitoes during their mating rituals.
Breakthrough in Malaria Vaccine Development
Also noteworthy is the recent success in developing a groundbreaking one-dose malaria vaccine, which has shown remarkable efficacy with up to 90% protection against the disease.
Conclusion
As we face these multifaceted challenges, staying informed is crucial. The intersection of viral infections, climate change, and vector-borne diseases demands our attention as we seek effective solutions to protect pregnant women and their babies from potential threats. What further discoveries lie ahead in our battle against these sinister pathogens? Stay tuned!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)