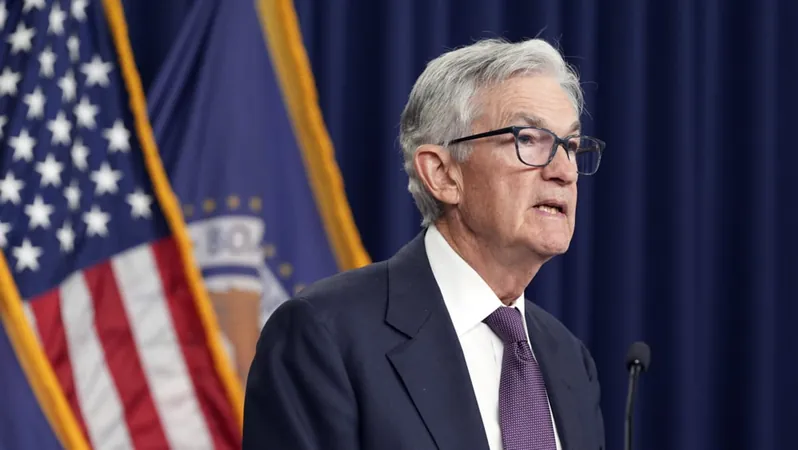

Fed Cuts Interest Rates: What Does This Mean for Your Wallet?
2024-12-18
Author: Nur
Introduction
In a decisive move on December 18, 2024, the US Federal Reserve announced a cut to interest rates, reducing the benchmark policy rate to the range of 4.25% to 4.50%. However, the central bank signaled that the pace of future cuts may slow significantly, citing a stable unemployment rate and persistent inflation levels that remain above target.
Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) Insights
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) articulated that the economy continues to show solid expansion, reflected in low unemployment rates, but inflation is still "somewhat elevated," complicating their monetary policy decisions. The Fed's new projections indicate only two anticipated quarter-percentage-point cuts by the end of 2025, a significant drop from the previously expected four cuts.
Inflation Forecast Changes
The adjustments in rate expectations coincide with a notable change in inflation forecasts. The Fed now anticipates inflation at 2.5% for the first year of the incoming Trump administration, revised up from 2.1%. This highlights an ominous trend as the full return to the 2% inflation target may not materialize until 2027, prompting concerns over a delayed and cautious approach to further rate cuts.
Fed Disagreement
Interestingly, Cleveland Fed President Beth Hammack dissented against the rate cut, advocating for a hold on the current policy rate, illustrating the division among Fed officials regarding the best path forward.
Market Reactions
Market reactions were swift; US Treasury bond yields saw an uptick, the dollar strengthened, and stock prices fell after the announcement. Whitney Watson, from Goldman Sachs Asset Management, commented on the Fed's decision to proceed with a gradual approach in the New Year, predicting that a rate cut in January may be skipped before resuming easing in March.
Political Climate and Economic Implications
Adding to the complexity is the uncertainty surrounding the incoming Trump administration. His administration's proposed tax cuts and policies on trade and immigration are viewed by many analysts as potential inflationary pressures. Although Trump won’t assume office until January 20, Fed officials insist they cannot tailor their monetary policies around campaign promises that may or may not be realized.
Economic Indicators
Key indicators show that economic growth is projected to remain above potential at 2.1% for the coming year, with inflation staying elevated for at least the next two years. The jobless rate is also set to remain low, never surpassing 4.3%.
Conclusion
As consumers, your financial landscape will inevitably be impacted. Reduced interest rates could mean lower borrowing costs for mortgages and loans, but the looming inflationary pressures and slower rate cuts suggest that maintaining a budget-conscious approach will be essential in the years ahead. Keep an eye on economic updates, as these shifts could have tangible effects on your finances.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)