Groundbreaking Geological Map of the Moon's Orientale Basin Unveiled – What Scientists Discovered Will Shock You!
2024-11-20
Author: Wei Ling
Groundbreaking Geological Map of the Moon's Orientale Basin Unveiled
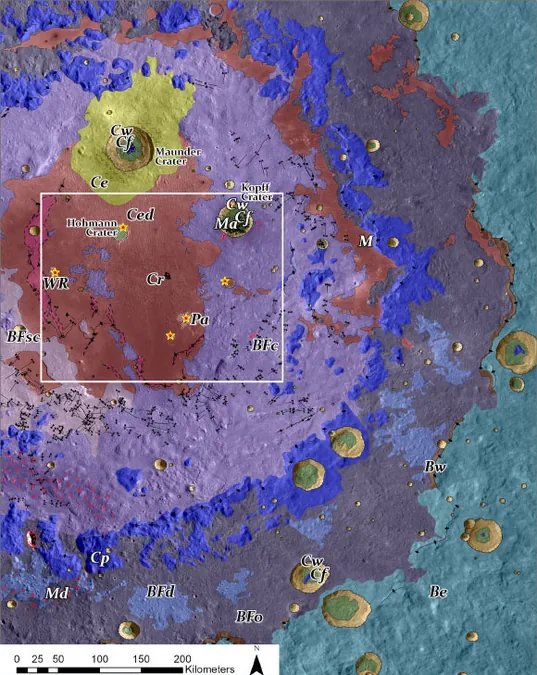
In a remarkable advancement for lunar science, researchers at the Planetary Science Institute have successfully created a high-resolution geological map of the Orientale basin, meticulously detailing its geological features at a 1:200,000 scale. This cutting-edge map serves a crucial purpose: to identify the most prominent and accessible deposits of impact melt – the remnants from a colossal asteroid strike that shaped this lunar landscape billions of years ago.
Approximately 3.8 billion years ago, a massive asteroid collided with the Moon with such force that it melted the surrounding rock, creating what scientists refer to as impact melt. This molten material eventually cooled and solidified, forming the complex multi-ringed crater we know as the Orientale basin today. Understanding these impact melt deposits is critically important; they allow scientists to apply laboratory techniques to precisely date the solidification of the melt, unveiling the timing of the original impact event.
However, a significant challenge remains. Subsequent geological processes, such as lava flows and minor impacts, have buried and disordered the original impact melt layers. Sorting through these layers can reveal vital historical information about the Moon's development, the evolution of the Solar System, and even the early conditions on Earth that may have facilitated the emergence of life.
Key researcher Kirby Runyon, along with his team, focused their efforts on the Orientale basin due to its unique geological age profile. “It’s a juxtaposition of old and young,” Dr. Runyon remarked, highlighting its 3.8 billion-year history that retains freshly exposed impact melt alongside more ancient, heavily cratered surfaces. The team's innovative approach not only refined the understanding of the Orientale basin but also tested strategies for identifying melt deposits in older, more eroded impact basins elsewhere on the Moon.
Utilizing a method referred to as BFsc, which designates smooth, cracked basin floor materials, the researchers pinpointed the original impact melt deposits. They strategically marked locations where smaller impact craters may have unearthed previously buried melt, establishing a potential correlation for age dating.
"If we can confirm that rocks from these noted locations are the same age as those from BFsc areas, we’ll have strong evidence to apply this sampling technique to more degraded basins," the team stated.
The implications of this study extend far beyond the Orientale basin itself. The techniques developed here could one day guide future sample-return missions, enabling scientists to gather rocks from other lunar locations with a high degree of confidence about their geological histories.
Published in the reputable Planetary Science Journal, this groundbreaking map not only highlights the complexities of lunar geology but also prompts an exciting frontier in our understanding of planetary impacts and their lasting consequences across the Solar System.
Don't miss out!
Dive deeper into the mysteries of the Moon and what these findings could mean for our quest to search for the universe's secrets!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)