Groundbreaking Insights into Chromatin Remodeling and its Impact on Gene Regulation
2025-04-03
Author: Mei
Chromatin remodeling is a fundamental process in gene regulation, directly influencing how our DNA is accessed for critical cellular functions. However, when this intricate mechanism malfunctions, it can trigger severe health issues, including cancer and a plethora of other diseases.
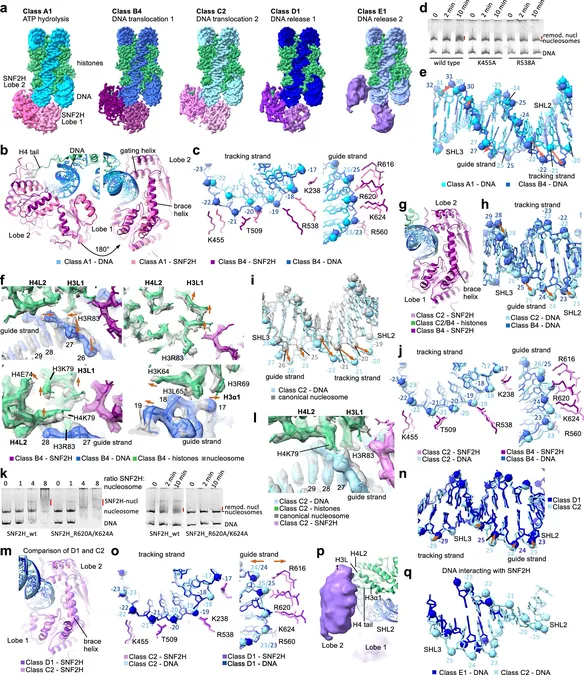
In an exciting development, researchers at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital have unveiled a detailed structural examination of chromatin remodeling using an advanced imaging technique known as cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). This pioneering study offers unprecedented insights into the mechanism of a prominent human chromatin remodeler, SNF2H, and has been published in the esteemed journal *Cell Research*.
Capturing the Dynamics of Chromatin Remodeling
Chromatin, the complex of DNA and histone proteins, forms nucleosomes that serve as the basic units of chromatin structure. One of the critical processes involved in chromatin remodeling is "nucleosome sliding." This process reposition nucleosomes, thereby regulating gene accessibility. Despite its significance, many aspects of how nucleosome sliding operates have remained elusive.
Dr. Mario Halic and his research team aimed to fill this knowledge gap by closely examining SNF2H in action. Previous studies mainly captured the remodeling enzyme at static points, akin to photographing a sculpture from various angles without showcasing its movement. In contrast, Halic's method allowed for real-time visualization of SNF2H as it interacted with nucleosomes under ATP conditions.
Unveiling the Mechanisms
Through methodical experimentation, the researchers successfully identified a total of 13 distinct structures of the SNF2H-nucleosome complex at different phases along the sliding process. By categorizing these structures into five distinct groups, they pieced together the intricate steps involved in nucleosome sliding. This comprehensive approach revealed a dynamic picture of how the remodeling enzyme operates.
Furthermore, the researchers probed the functional significance of specific interactions within the chromatin remodeling process by introducing targeted mutations and cross-linking agents—creating artificial restraints to study their impacts on SNF2H's function. This analytical strategy helped clarify earlier conflicting observations and resulted in a well-rounded understanding of the nucleosome sliding mechanism and its ramifications on gene regulation.
Implications for Human Health
"Nucleosomes carry all the genetic information inside the nucleus of the eukaryotic cell. Chromatin remodelers enable the cell to access and regulate that information," co-first author Dr. Deepshikha Malik emphasized. "Understanding the mechanics of how these remodelers operate on nucleosomes is essential for deciphering how our genome is expressed."
A deeper understanding of chromatin remodeling could yield significant implications for treating diseases linked to genetic disruptions. As ongoing research continues to unveil the complexities of gene regulation, it paves the way for potential therapeutic strategies that target remodeling processes, offering new hope in the battle against genetic disorders and malignancies.
This groundbreaking study not only enriches our understanding of chromatin biology but also highlights the critical role that chromatin remodelers play in the overarching narrative of gene expression and human health. Stay tuned for more updates as researchers continue to uncover the mysteries of our genetic code!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)