Groundbreaking New Drug NXP800 Shows Promise for Prostate Cancer Treatment
2025-01-10
Author: Li
In a recent thrilling breakthrough for prostate cancer treatments, researchers from The Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) in London have unveiled that the experimental drug NXP800, currently undergoing trials for ovarian and bile duct cancers, may offer new hope for patients with prostate cancer that has become resistant to conventional hormone therapies.
The Challenge of Treatment Resistance
Many patients diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer initially respond well to hormone therapies such as enzalutamide and abiraterone. However, nearly all patients eventually develop resistance, leading scientists to urgently seek effective alternatives. This innovative drug, NXP800, targets a critical cellular pathway known as the Heat Shock Factor 1 (HSF1) pathway. This pathway serves as a "master switch," enabling cancer cells to survive the physiological stresses associated with tumor progression and growth.
Linking Heat Shock Proteins to Survival Rates
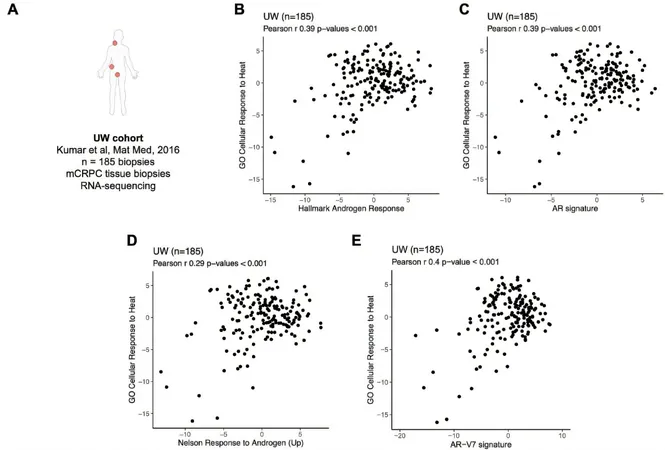
In a comprehensive analysis of 439 advanced prostate cancer samples, the researchers identified a disturbing correlation: higher levels of heat shock proteins, which assist cancer cells in evading stress, were linked to increased androgen receptor activity—a major driver of prostate cancer growth—and poorer patient survival outcomes. Remarkably, patients exhibiting elevated levels of these proteins had an average survival time of just 22 months, compared to 33.5 months for those with lower levels.
NXP800: The Game Changer
Promising laboratory tests revealed that NXP800 dramatically inhibits the proliferation of prostate cancer cells, including those resistant to enzalutamide. In controlled experiments, patient biopsies cultured as mini-tumors displayed significantly less growth when treated with NXP800, showcasing its potential to outpace traditional hormone therapies, which showed only minor effects even in high concentrations.
Impressive Results in Mouse Studies
Further validation came from animal studies where NXP800 distinctly slowed tumor growth in mice afflicted with hormone therapy-resistant prostate cancers. While untreated control tumors doubled in size within just 38 days, only 37.5% of NXP800-treated tumors reached the same growth size in that timeframe—a clear indication of the drug's efficacy.
Future Perspectives and Ongoing Research
The team at ICR is hopeful that these groundbreaking findings will prompt additional clinical trials to evaluate NXP800 as a viable treatment for advanced prostate cancer. Ongoing mechanistic studies aim to further clarify how NXP800 disrupts the HSF1 pathway and modulates the unfolded protein response, which is vital to understanding patient responsiveness to the treatment.
NXP800 has already garnered Fast-Track and Orphan Drug Designations from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its potential treatment value in certain cancers. Its consideration for advanced prostate cancer marks an exciting development in the ongoing quest for effective cancer therapies.
Expert Opinions and Future Directions
Dr. Adam Sharp, co-leader of the study, articulated a cautious optimism about targeting the heat shock response pathway, describing it as a promising new horizon in confronting the challenges posed by drug resistance. Professor Johann de Bono emphasized that the research identifies a critical pathway for intervention, hinting at the potential for improved prognosis for patients facing advanced cancer.
Additionally, Simon Grieveson from Prostate Cancer UK noted the importance of continued research focus on alternative treatment strategies. He remarked that if these findings translate successfully into clinical applications, they could significantly enhance the quality and length of life for men battling hormone-resistant prostate cancer.
What Lies Ahead: A New Era of Treatment?
The pursuit of NXP800 represents a beacon of hope for patients who have run out of options. With promising results on the horizon, the medical community eagerly anticipates the launch of clinical trials, poised to redefine therapeutic strategies for advanced prostate cancer and ultimately offer patients more time with their loved ones. As one door closes on current treatments, a new door may well be opening, setting the stage for potentially transformative developments in cancer care.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)