Groundbreaking Research Unveils Secrets of Glucagon: A Game Changer for Diabetes and Obesity Treatments!
2024-10-02
Author: Arjun
Monash University researchers have made a remarkable breakthrough in understanding the hormone glucagon, shedding light on its potential to revolutionize treatments for obesity and type 2 diabetes—conditions that impact billions globally.
Although glucagon has been recognized for over a century, the mechanics of how it functions have remained a mystery until now. A collaborative international team, spearheaded by the Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute, leveraged innovative pre-clinical models and meticulous cellular experiments utilizing advanced viral and molecular technologies to unlock new therapeutic avenues.
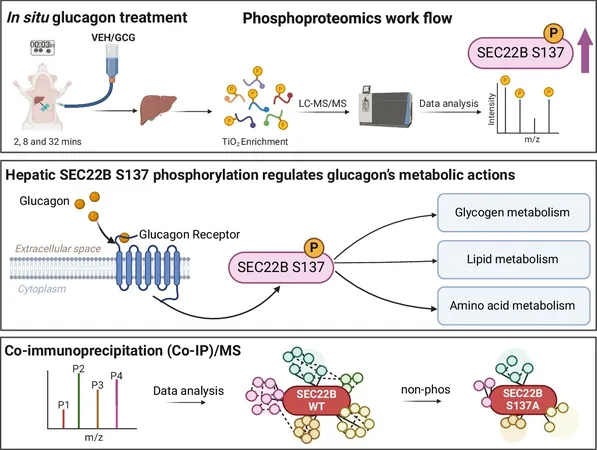
Their groundbreaking findings, published in the prestigious journal *Nature Communications*, unveil how glucagon transmits signals within liver cells, and – for the very first time – elucidate the intricate dynamics of vesicle trafficking involving a key protein known as SEC22B. This discovery marks a significant leap in our comprehension of glucagon’s role in metabolic processes.
Lead researcher, Associate Professor Adam Rose, who heads the Nutrient Metabolism and Signaling Lab at the Biomedicine Discovery Institute, emphasized the implications of this research: “By clarifying the mechanisms behind glucagon's action, we can potentially engineer more targeted and effective therapies for metabolic diseases like obesity and type 2 diabetes. This not only promises to enhance the quality of life for millions but also has far-reaching economic and societal benefits.”
Interestingly, despite glucagon being known for over 100 years, its signaling pathways in the liver had remained largely uncharted territory. Glucagon is secreted by certain pancreatic cells, playing a pivotal role in elevating blood glucose levels—an essential aspect of the type 2 diabetes conundrum. While glucagon raises blood sugar, insulin works to lower it, creating a delicate balance vital for maintaining glucose homeostasis.
“Although glucagon is a well-established hormone, the specifics of how it communicates within the liver to produce its diverse effects were poorly understood,” explained Associate Professor Rose. “Our findings dramatically alter this understanding and pave the way for new therapeutic possibilities.”
The research highlights that glucagon-based treatments are increasingly being recognized as premier options for managing obesity, type 2 diabetes, and fatty liver disease. The team’s inquiry is just the beginning; they uncovered that the vesicle trafficking protein plays a central role in mediating nearly all of glucagon’s metabolic impacts, opening a treasure trove of opportunities for further investigation.
As the fight against metabolic syndromes continues, researchers are optimistic that this newfound knowledge will lead to the development of next-generation treatments that could improve patient outcomes significantly. With billions of lives at stake, the implications of this research extend far beyond the laboratory—poised to transform the landscape of metabolic disease therapies forever!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)