HPV Genotypes Uncovered: Disturbing Trends in Mashhad, Iran (2022-2023 Study)
2024-10-07
Author: Wei
Introduction
The Human Papillomavirus (HPV) continues to lurk as a leading villain in the story of cervical cancer and other malignancies, including oropharyngeal, anal, and genital cancers. As researchers endeavor to unravel the prevalence and types of HPV affecting populations, new findings from Mashhad, Iran, shed light on a chilling truth: nearly one in three individuals in this study exhibited signs of HPV infection. This article dives into the results of a comprehensive study conducted between 2022 and 2023 to illuminate HPV's prevalence and its most common genotypes in this region.
Study Overview and Methodology
In an extensive investigation, 428 samples were analyzed, predominantly from women (89.3%) and a smaller proportion of men (10.7%). Researchers collected cervical swabs from females and urine samples from males in private laboratories across Mashhad. The study administered DNA extraction and genotype identification through sophisticated methods, with the results delivering revelations about the distribution of HPV among these individuals.
Shocking Findings and Implications
Of the 428 participants, a staggering 30.1% tested positive for HPV, highlighting a significant public health concern. The study revealed that HPV-6 emerged as the most prevalent genotype (10.3%), followed closely by HPV-16 (8.7%) and HPV-51 (7.7%). While the vaccines cover HPV-6 and HPV-16, the discovery of high-risk genotypes—notably HPV-51 and HPV-39—ring alarm bells for future cancer risks, especially since these types are not effectively prevented by the current available vaccines.
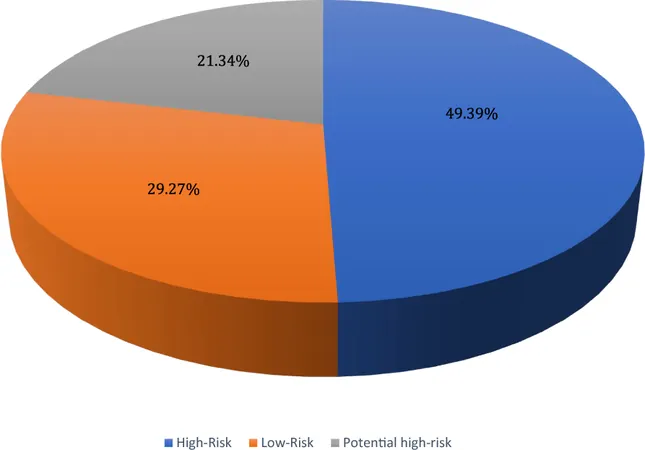
Interestingly, the infection rates among genders showed minimal disparity, with HPV positivity at 30.1% in females and 30.4% in males. The study also noted that nearly half (49.4%) of the HPV-positive individuals carried at least one high-risk genotype—a statistic that cannot be overlooked as it expands the potential for future oncogenic consequences.
The Challenge of Vaccination and Awareness
Despite high infection rates, HPV vaccination remains extraordinarily underutilized in Iran. The figures indicate significantly low uptake of HPV vaccines, due in part to cost barriers and limited availability. The importance of the HPV vaccine is underscored by its potential to prevent the majority of cervical cancers if administered before individuals become sexually active.
The Iranian health landscape is fraught with challenges, highlighted by limited sexual health education and rising rates of high-risk sexual behavior among youth. Notably, the traditional stigma surrounding sexual health discussions exacerbates the lack of awareness, resulting in a marked increase in HPV infections.
Nationwide Public Health Concerns
Cervical cancer stands as a critical health threat, with about 604,000 new cases and 342,000 deaths worldwide annually. The study conducted in Mashhad mirrors alarming trends seen in national and global statistics, echoing the need for expanded and effective preventive measures.
Given that Mashhad is a heavily populated city and a pilgrimage destination, the interplay of multiple factors such as urban migration, sexual behavior, and healthcare access complicates the HPV scenario. The urgency for cervical cancer screening programs and government-supported vaccination initiatives is more critical than ever.
Conclusion: The Need for Action
This study lays bare the urgent requirement for targeted public health interventions to combat HPV-related health risks. To enhance awareness and pave the way for better health outcomes, it is essential to launch comprehensive vaccination programs and educate the community about the importance of regular screenings. The evidence emerging from Mashhad thus serves as a call to action for both health authorities and communities to tackle the looming threat of HPV head-on.
Final Thoughts
With HPV posing a substantial risk worldwide—and particularly among populations in Iran—the message is clear: immediate action is essential. As we move forward, a strategic focus on vaccination, screening, and education will be pivotal in changing the tide against HPV and reducing its associated cancer risks.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)