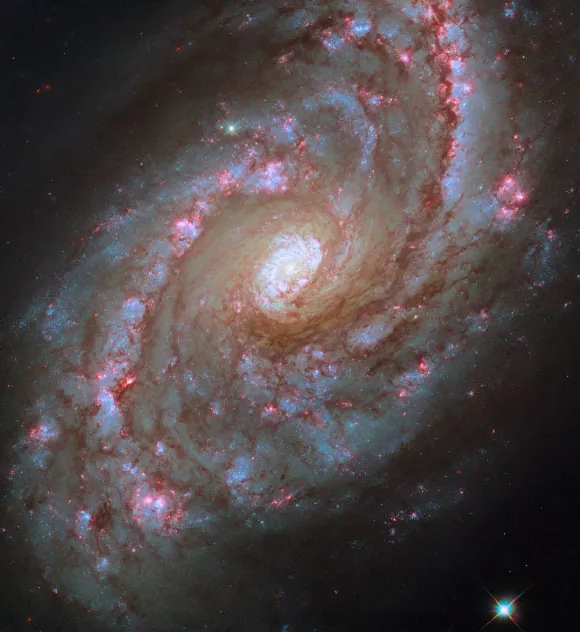

Hubble Space Telescope Unveils Stunning Starburst Regions in NGC 5248
2024-10-07
Author: Wei Ling
Hubble Space Telescope Captures NGC 5248
The Hubble Space Telescope, equipped with its Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3), has captured a breathtaking new image of the grand design spiral galaxy known as NGC 5248. Located about 42 million light-years away in the constellation Boötes, this galaxy is not only a sight to behold but also a fascinating subject for astronomical research.
Characteristics of NGC 5248
NGC 5248, also referred to by several designations including Caldwell 45 and LEDA 48130, boasts an impressive diameter of 95,000 light-years. It was first identified by the prominent German-born British astronomer William Herschel on April 15, 1784, and remains an important member of its galactic group.
With an apparent magnitude of 10, NGC 5248 can be observed using a small telescope, making it accessible to both novice star-gazers and experienced astronomers, although its brightness may not be overwhelming.
Starburst Activity in NGC 5248
One of the most remarkable features of NGC 5248 is its nuclear rings, which are hotspots of intense starburst activity. According to Hubble astronomers, 'NGC 5248 is classified as a ‘grand design’ spiral galaxy, characterized by its strikingly prominent spiral arms that extend from the core outward into the disk.' Additionally, a subtle bar structure can be discerned in the galaxy's center, linking the inner ends of its spiral arms, a detail that is less visible in Hubble's optical images.
Galactic Dynamics and Evolution
The dynamics within NGC 5248 are shaped by structures that disrupt the galaxy's rotational symmetry, influencing the movement of matter throughout. These factors play a critical role in its evolutionary process over time. Astronomers note that such structures facilitate the transfer of gas from the outskirts of the galaxy to regions of star formation and possibly towards the central black hole, igniting the activity of the galaxy's core.
Observing Star Formation Regions
NGC 5248 is particularly captivating due to its extraordinarily vivid regions of star formation, which are dominated by young stellar populations. Importantly, the galaxy features two active, ring-like starburst regions surrounding its nucleus, teeming with young star clusters. Intriguingly, while a nuclear ring typically hinders gas from moving deeper into a galaxy's core, NGC 5248's second inner ring signifies the intense and dynamic flows of matter and energy occurring within it.
Conclusion: A Galaxy Worth Observing
For both professional astronomers and amateur enthusiasts, the easily observable starburst regions make NGC 5248 a prime candidate for study and admiration. This galaxy not only highlights the beauty of the universe but also offers insights into the processes that govern star formation and galactic evolution.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)