Major Breakthrough: Researchers Reveal the Most Comprehensive Primate Family Tree Ever!
2024-12-17
Author: Wei
Major Breakthrough: Researchers Reveal the Most Comprehensive Primate Family Tree Ever!
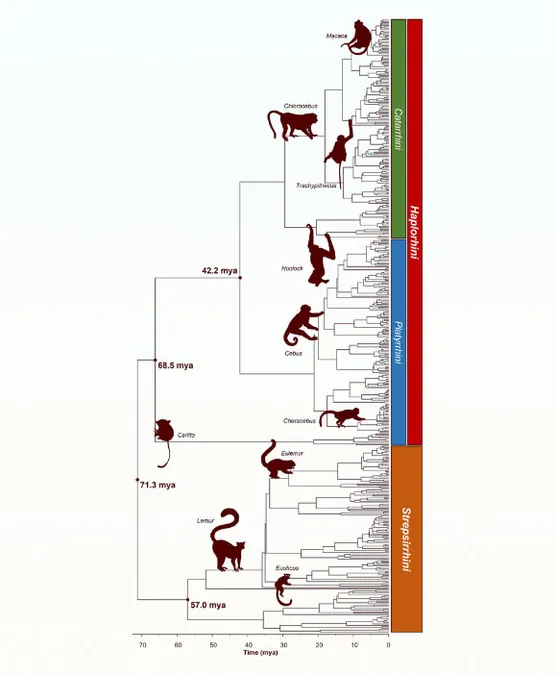
In an exciting development, researchers have unveiled a new family tree for primates, a diverse and captivating order that includes apes, monkeys, tarsiers, and lemurs. The findings, which promise to reshape our understanding of primate evolution, involve 455 species—marking the most detailed evolutionary structure we have of these extraordinary animals.
Primates are amongst the most familiar and studied groups in the animal kingdom, showcasing remarkable behaviors such as chimpanzees ‘fishing’ for termites with specialized sticks and orangutans using leaves as protective gloves against thorny durian fruit. Despite being point of intrigue for decades, the complete molecular evolutionary relationships among primates have remained elusive.
The new research, led by Dr. Jack Craig and colleagues at Temple University, tackles this gap head-on. Their comprehensive molecular phylogenetic tree, or ‘timetree,’ aggregates data from over 4,000 studies, accumulating knowledge that allows scientists to trace back the history of primates effectively. Until now, only about a fifth of the primate family tree was satisfactorily resolved.
Dr. Craig emphasized the importance of these timetrees, stating, “They are crucial not only for understanding evolutionary history but also for taxonomic and systematic studies to catalog new species.” With biodiversity under threat from rapid extinction rates, well-structured evolutionary trees are vital for identifying conservation priorities.
One of the intriguing findings from their work is the rate of speciation across various primate lineages. By analyzing the new timetree, researchers concluded that the number of species in different primate clades is predominantly influenced by their evolutionary age rather than unique rates of new species formation. This revelation suggests that older lineages simply accrue more species over time, thereby reshaping our understanding of primate diversity.
In addition to highlighting evolutionary relationships, this extensive timetree serves various fields like biogeography and historical ecology, making it an essential tool for future research. It is poised to aid in untangling further mysteries of primate evolution and will support conservation efforts by clarifying which species and lineages are most at risk.
The findings have been published in the journal, *Frontiers in Bioinformatics*, symbolizing a significant stride in primate research. With this breakthrough, researchers aim to inspire new avenues of inquiry into primate evolution and conservation—underscoring that even the most well-known species still hold secrets waiting to be uncovered. Stay tuned for more updates as this evolutionary saga unfolds!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)