
Mysterious Vanishing Dark Spot on Enceladus: What Could It Mean for Life Beyond Earth?
2024-12-15
Author: Siti
Introduction
Saturn, known for its stunning rings and an astonishing variety of natural satellites, boasts an impressive 146 moons. Among these, Enceladus stands out, captivating the interest of scientists eager to uncover the secrets it may hold about extraterrestrial life. This ice-covered moon is not just another celestial body; it might be a gateway to understanding life beyond our planet due to its subsurface ocean, which potentially contains essential ingredients for life.
The Mystery of the Dark Spot
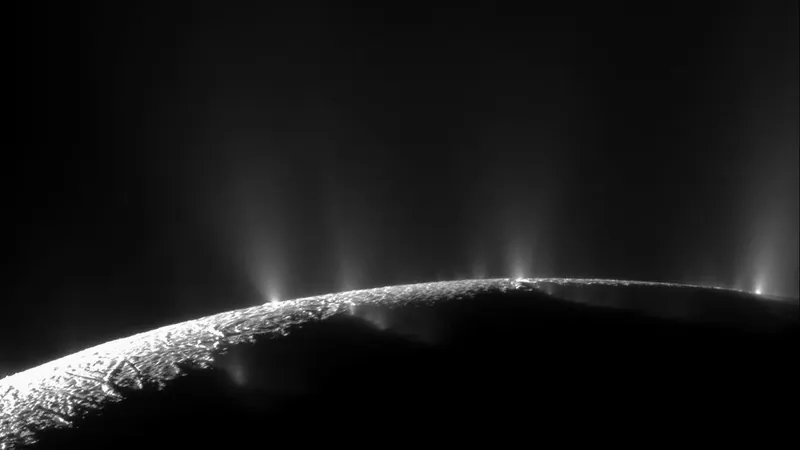
Recent studies have intensified the intrigue surrounding Enceladus, particularly with the discovery of a perplexing dark spot on its surface that seems to be fading away over time. This enigma was a hot topic at the 2024 American Geophysical Union meeting held in Washington, D.C., where scientists gathered to deliberate over cosmic mysteries.
Insights from Cynthia B. Phillips
Planetary geologist Cynthia B. Phillips from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory provided insights into the origin of this dark spot. Detected first in a 2009 image, it was found to be nearly absent in a 2012 observation. This unusual characteristic is striking given that Enceladus has a high reflectivity, or albedo, leading researchers to question why a dark spot would even exist on its surface.
Possible Explanations
As Phillips explained, extensive image comparisons revealed that the dark spot, roughly a kilometer wide, diminished in size over the observed years rather than appearing more pronounced. This defies expectations, prompting scientists to explore various hypotheses for its origin. They ruled out possibilities such as mere shadows or variations in imaging resolution.
Theories About the Dark Spot's Nature
What could this curious feature represent? One leading theory is that it could be a crater filled with a darker material leftover from an impact. Alternatively, there’s speculation about it being an indicator of sub-surface phenomena, revealing more about the moon’s geological activity than previously understood.
Impact of Icy Plumes
The fading of the dark spot might also suggest that icy plumes—massive jets of water vapor and ice particles shooting into space from beneath the moon's surface—could be covering it. If true, this would imply that such deposits accumulate more rapidly than anticipated, potentially changing our understanding of Enceladus's geological processes.
Contradictions and Questions
However, contradictions arise: the speed of the dark spot’s disappearance seems too quick for the deposition models currently in use. According to calculations, covering such an area typically should take around 100 years. This anomaly sparks discussions among scientists about different factors at play, such as collision with tiny particles from Saturn's E ring, which could contribute to the coverage of the dark spot.
Conclusion and Future Investigations
Despite the progress in analyzing this feature, many questions remain unanswered. What drives the deposition rates? Is the E ring significantly impacting this process? And most importantly, what is the true nature of the dark spot itself? Whatever the outcome, the implications of this discovery are significant. The dark spot on Enceladus may hint at exciting new understandings of the moon's activity and could offer valuable insights into the potential for life elsewhere in our solar system. As we continue to investigate, Enceladus remains a focal point in the quest to answer humanity’s age-old question: Are we alone in the universe? Stay tuned for further revelations about this intriguing moon!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)