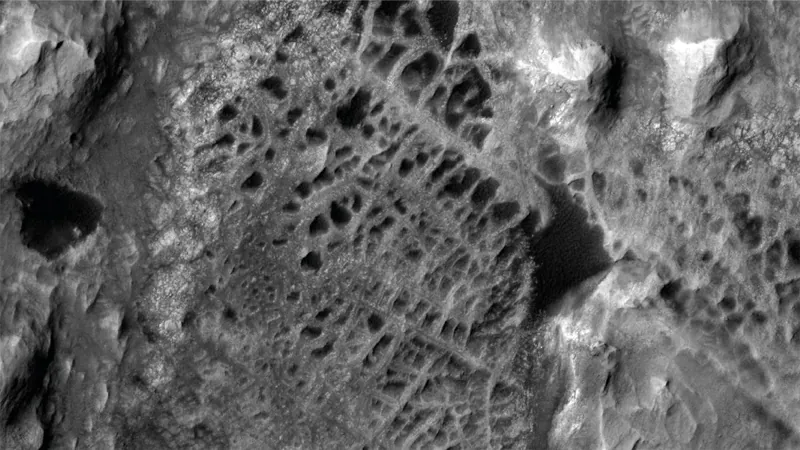

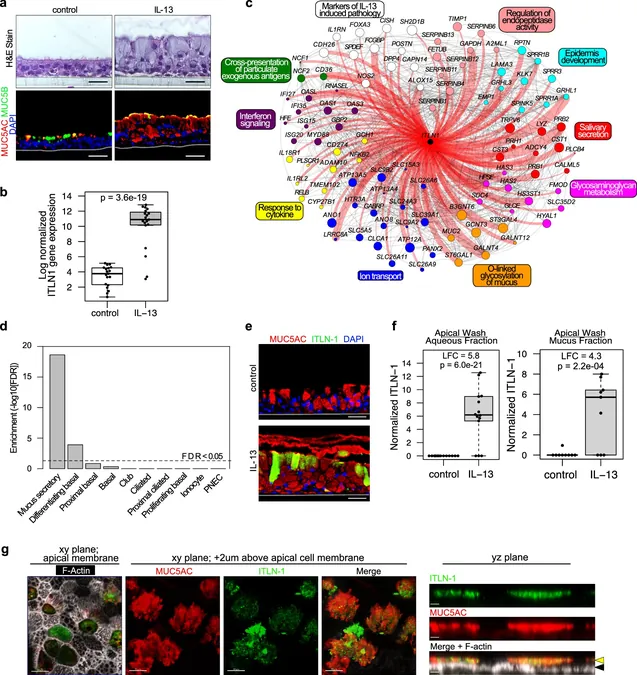
NASA's Curiosity Rover Set to Unravel Mars' Mystical Spiderweb Patterns
2024-11-26
Author: Mei
Unveiling the Secrets of Mars
If you thought Mars was just a barren landscape, think again! NASA scientists are gearing up for an exciting exploration that could redefine our understanding of the Red Planet. Last week, the space agency revealed that its iconic Curiosity rover is set to embark on a journey to the enigmatic foothills of Mount Sharp, where a striking formation of spiderweb-like patterns, never before seen on such a scale, awaits discovery.
These intriguing structures, called "boxwork," are believed to have formed billions of years ago through mineral deposits left by ancient groundwater flows. This geological phenomenon could hold vital clues about the potential existence of microbial life on Mars in its distant past.
A Closer Look at the Boxwork
Previously, our best view of this extraordinary formation came from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, which captured images of the boxwork using its advanced HiRise camera back in 2006. As Curiosity gears up for its adventure, scientists are eagerly anticipating their first up-close observations of these stunning geological features.
Located in the shadow of Mount Sharp, a towering three-mile-high mountain at the heart of Gale Crater, the boxwork stretches an astonishing six to twelve miles. Its unique appearance is accentuated by ridges that stand out against the dark sand filling their voids, making it a truly remarkable sight.
While boxwork formations can also be found on Earth, they are typically small, occurring in caves or on cliffsides. The sheer scale of the Martian boxwork is unmatched, providing a rare opportunity for planetary scientists to study geological processes and the history of water on Mars.
Potential Life on Mars?
The implications of this research go beyond mere curiosity. Scientists believe that if Mars ever supported life, evidence may still be trapped within these boxwork formations. Kirsten Siebach, a planetary scientist at Rice University who is part of the Curiosity team, emphasized the importance of the minerals within the ridges, suggesting they may have crystallized in warmer, aqueous environments.
"This region may have been home to conditions similar to those on early Earth, where microbial life thrived. It's a thrilling opportunity to explore an area with such potential for discovery," Siebach asserted.
The Curiosity rover is expected to arrive at its destination by 2025, and the excitement is palpable among the scientific community. As Curiosity ventures into this uncharted territory, we may soon unlock the secrets of Mars and gain insights that could reshape our understanding of life beyond Earth.
Stay Tuned!
Keep your eyes peeled for updates as NASA's Curiosity rover unveils the mysteries of the Martian landscape. Who knows what astonishing discoveries await?


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)