New Insights into the Online Health Information-Seeking Behavior of Breast Cancer Patients: What You Need to Know!
2025-01-03
Author: Siti
Introduction
A recent scoping review sheds light on the online health information-seeking (OHIS) behaviors of breast cancer patients and survivors, a group that increasingly turns to digital platforms for crucial health information. With breast cancer being the second most common cancer worldwide, understanding how patients interact with online resources is essential for improving their healthcare experiences and outcomes. This review not only highlights key findings but also uncovers significant gaps in existing research and sets the stage for future studies.
Review Purpose and Methodology
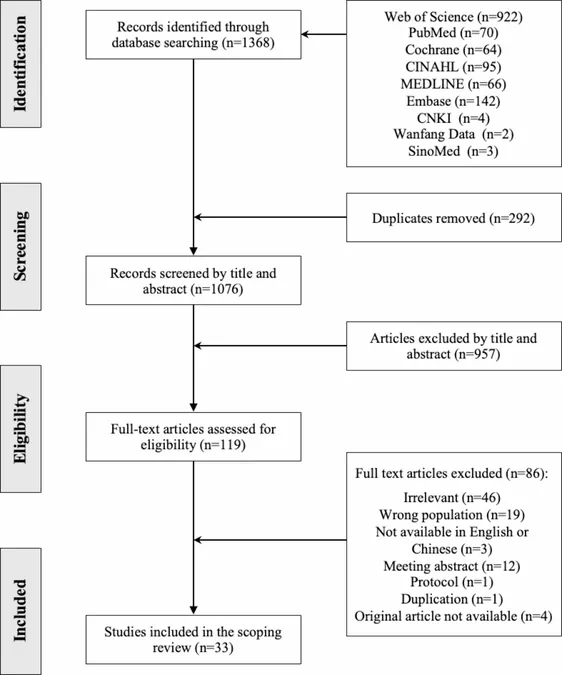
This comprehensive review aimed to summarize OHIS behaviors in breast cancer patients and identify areas for further research. Conducted following a structured methodology outlined by Arksey and O'Malley, researchers reviewed literature from multiple reputable databases including PubMed, Web of Science, and Cochrane, covering publications from January 2014 to August 2023. Out of 1,368 articles found, only 33 met the strict inclusion criteria for the study.
Key Findings
The review identified three major themes related to OHIS: the behavior itself, factors influencing it, and interventions designed to improve it. Patients often sought out information from national cancer organizations, various search engines, and social media platforms. They were primarily looking for knowledge regarding treatment options, prognosis, and general cancer information. However, many expressed frustrations over the accuracy and reliability of online content, emphasizing a need for better quality assurance in digital health resources.
Understanding Patient Behavior
OHIS behavior varied significantly among patients, influenced by factors such as age, education level, and psychological state. Younger, more educated individuals with higher income levels tended to seek information online more frequently. Interestingly, patients at different stages of their treatment sought information about various topics; for example, those post-surgery were less engaged than those earlier in their treatment journey.
A shocking trend emerged: while most patients used the internet to find information, less than half of them consulted healthcare professionals about their online findings. This highlights a gap where patients are not fully integrating their digital research with their medical care, potentially leading to misinformation and misinformed decisions about treatment options.
Interventions and Future Directions
The review revealed that despite the rising trend in seeking online health information, there remains a significant inadequacy in the intervention programs designed to support patients. While a few studies have explored web-based interventions, most of these programs have not undergone thorough evaluation. Future research must develop targeted digital interventions tailored to the specific needs of breast cancer patients, integrating multimedia resources and ensuring that the information is both accessible and understandable.
Breakthrough Insights
The review underscores the necessity of improving the legibility and reliability of information on cancer-related websites. Many patients struggle with medical jargon, and efforts should be made to provide information in simpler language to reach a broader audience. Furthermore, enhancing the functionality and accessibility of these online resources could directly impact quality of care and patient satisfaction.
As we plunge deeper into the digital age, many patients have turned to social media for support and information, solidifying it as a platform for not only sharing experiences but also as a key resource for health information. Interestingly, younger patients were found to particularly benefit from these platforms, finding community support among fellow survivors.
Conclusion
The exploration of OHIS behavior among breast cancer patients reveals both its vital role in the healthcare journey and the significant gaps that need addressing. Online health resources hold the potential to empower patients, improve their understanding, and ultimately enhance health outcomes. It is vital for both researchers and healthcare providers to recognize these findings and tailor their approaches accordingly, ensuring patients are not only informed but also supported through their cancer journeys.
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)