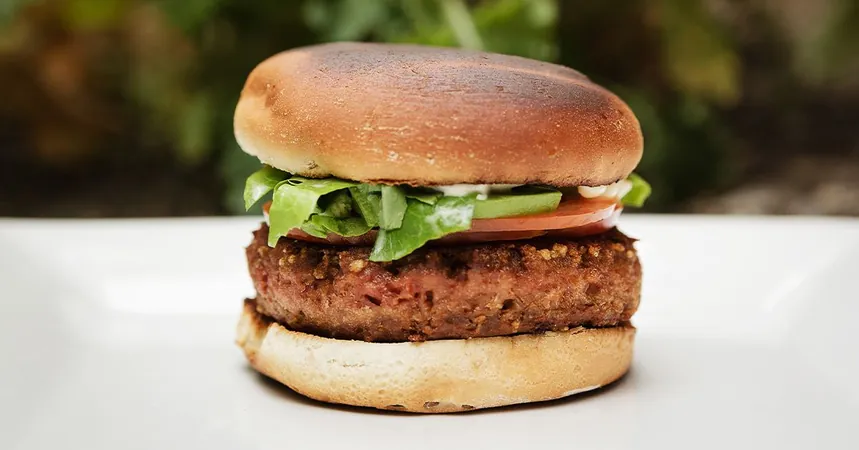

New Study Reveals Alarming Link Between Plant-Based Meat Alternatives and Mental Health Risks in Vegetarians
2024-12-20
Author: Siti
Introduction
Recent findings from a groundbreaking study have unveiled a concerning trend among vegetarians consuming plant-based meat alternatives. The research, published in *Food Frontiers*, indicates that individuals who incorporate these processed foods into their diets may face a staggering 42% increased risk of depression, alongside notable signs of inflammation.
Rising Popularity of Plant-Based Alternatives
Plant-based meat alternatives—including products like tofu, tempeh, and meatless burgers—are gaining popularity as more people opt for diets perceived as healthier and more environmentally friendly. These substitutes, often derived from soy, nuts, or even fungi, present appetizing options for those wishing to steer clear of traditional meat sources.
Key Findings of the Study
While the study observed that overall consumption of plant-based alternatives posed no significant health risks, researchers highlighted a worrying correlation between these products and mental health implications for vegetarians. Nophar Geifman, PhD, a health and biomedical informatics professor at the University of Surrey, states, 'The findings suggest that while plant-based meat alternatives can be part of a balanced diet, the link between these foods, inflammation, and depression merits further scrutiny.'
Study Methodology
The study evaluated the health of over 3,300 non-meat eaters—excluding pescatarians—over an average span of 14 years. Participants were categorized into two groups based on their consumption of plant-based alternatives. Those who consumed these processed foods displayed elevated levels of inflammation measured by C-reactive protein (CRP) and slightly higher blood pressure levels, although overall heart health risks were reportedly unchanged.
Previous Research Correlation
This research builds on previous studies that indicated that a high intake of ultra-processed foods could be linked to an increase in depression. Notably, the 2023 research pointed out that consumption of artificial sweeteners and beverages sweetened artificially may be particularly harmful.
Mixed Results for IBS
Interestingly, while individuals consuming plant-based meat alternatives reported a higher risk of depression and inflammation, the new study also found a silver lining: those who opted for these substitutes had a 40% lower risk of developing irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) compared to non-consumers.
Expert Perspectives
Experts, including registered dietitian Amy Kimberlain, warn of the limitations in this study, noting that most participants were white and female, potentially limiting the applicability of findings across diverse populations. Additionally, dietary data was primarily gathered at the study’s outset, leaving room for changes in eating habits over time to go unrecorded.
Recommendations for Healthy Plant-Based Diets
Despite these cautionary findings, Kimberlain emphasizes that transitioning to a vegetarian diet can be done healthfully by focusing on whole, minimally processed plant foods rather than relying solely on meat alternatives. She encourages incorporating a variety of proteins, such as beans, nuts, and whole grains, into meals to support overall health and reduce risks associated with depression and inflammation.
Conclusion
As the popularity of plant-based diets continues to rise, these findings serve as a critical reminder for vegetarians to approach their dietary choices with mindfulness, ensuring a balance of whole foods while being aware of the potential implications of processed alternatives. Further research is essential to unravel the intricate relationship between diet, mental health, and inflammation as we move towards healthier eating habits.
Stay tuned for more updates as scientists delve deeper into the world of plant-based nutrition and its effects on our well-being!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)