
Perseverance Rover Reaches New Heights: Unlocking Mars' Ancient Secrets
2024-12-18
Author: Wei Ling
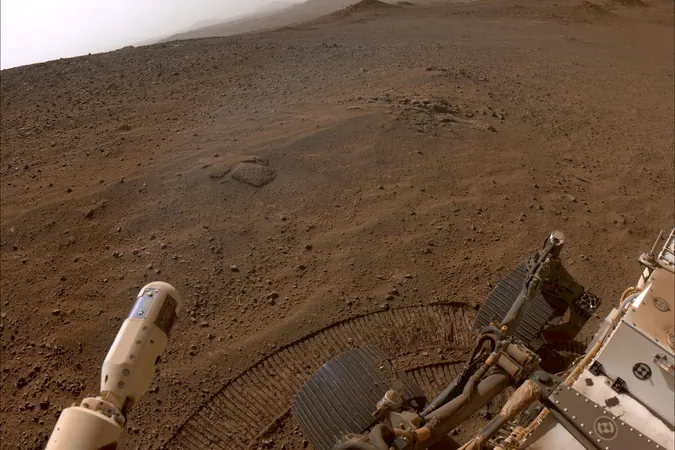
NASA's Perseverance Mars rover has reached a remarkable milestone as it crested the top of Jezero Crater’s rim, an imposing geological structure that is pivotal to our understanding of Mars' history. On December 10, 2024, the rover captured stunning panoramic images from a vantage point named “Lookout Hill,” signaling the successful conclusion of a months-long climb that saw it ascend 1,640 vertical feet through challenging terrain. This ascent, equivalent to scaling a steep 20% gradient, took about three and a half months and involved numerous stops for scientific observations.
Since its landing in Jezero Crater in February 2021, Perseverance has embarked on four dedicated scientific campaigns: “Crater Floor,” “Fan Front,” “Upper Fan,” and “Margin Unit.” The current campaign, termed the “Northern Rim,” focuses on exploring the geological features on the northern edge of Jezero Crater. Over the course of the next year, the rover is anticipated to traverse approximately four miles, investigating sites of significant geological interest.
The road to the Northern Rim has not been easy, as the terrain posed unique challenges that tested the rover's navigational capabilities. Steven Lee, the deputy project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), praised the team for their ingenuity in maneuvering through the rugged landscape, noting even attempts to drive backwards to address specific obstacles. Perseverance has shown remarkable resilience and is primed for the scientific investigations ahead.
Ken Farley, the project scientist from Caltech, emphasizes the scientific importance of this mission phase. The Northern Rim area is crucial as it contains some of the oldest rocks discovered in the solar system, formed nearly 3.9 billion years ago during a massive impact event that created Jezero Crater. These geological samples could hold vital clues about Mars' early crust and its environmental conditions, enhancing our understanding of both Mars and Earth.
Following its successful climb, Perseverance is now en route to “Witch Hazel Hill,” a geological feature located just 1,500 feet downhill on the crater's opposite side. This site promises an impressive 330 feet of layered rock strata—each layer offering a glimpse into the ancient Martian landscape, akin to flipping through the pages of a historical book about Mars.
Excitement builds as the rover prepares to leave Witch Hazel Hill for “Lac de Charmes,” located about two miles to the south. This area is particularly intriguing for scientists since it lies on a plain thought to have been minimally impacted by the formation of Jezero Crater, providing a pristine opportunity to study Martian geology.
After analyzing Lac de Charmes, Perseverance intends to return to the rim to investigate a fascinating outcrop known as megabreccia. These large rock fragments could be remnants of ancient bedrock disrupted during the Isidis impact, which altered the Martian landscape over 3.9 billion years ago, creating one of the largest impact basins in the solar system.
Beyond its geological explorations, the Perseverance mission has a significant focus on astrobiology. The rover aims to cache samples that could hint at past microbial life, providing critical information for future human missions to Mars. Perseverance will help lay the groundwork for understanding the planet's climate and geology while running in parallel with NASA's Mars Sample Return Program, in collaboration with the European Space Agency.
Part of NASA's ambitious moon-to-Mars exploration framework— which includes preparations for Artemis missions to the Moon—this rover is paving the way for humanity's eventual exploration of the Red Planet. With each finding, Perseverance is not just extending our reach across the cosmos but is also unveiling the mysteries of our own planetary history. Stay tuned, as the rover embarks on its next scientific journey!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)