Revolutionary AI Algorithm Doubles Stroke Timing Accuracy - Could Save Lives!
2024-12-17
Author: Wei
Introduction
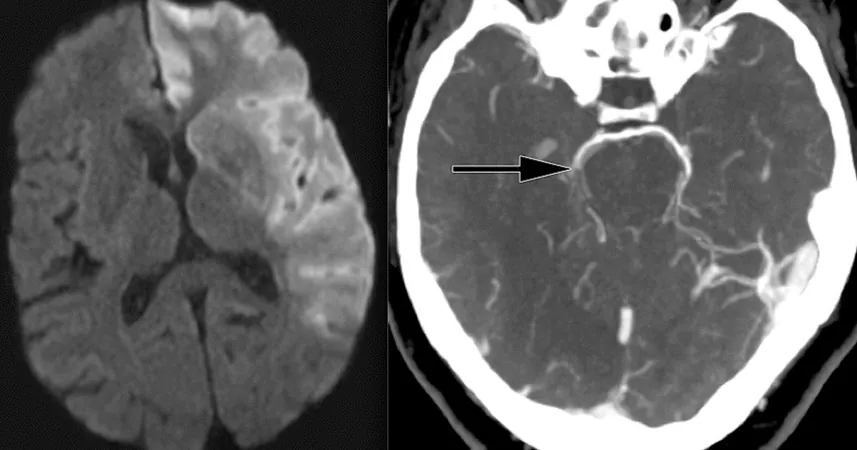
A groundbreaking new artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm is set to transform the way medical professionals predict the timing of strokes using CT imaging. Recent findings indicate that this innovative algorithm is not only doubling the accuracy of stroke onset estimations compared to traditional visual assessments but also holds immense potential to improve patient outcomes significantly.
Research Findings and Methodology
Published in NPJ Digital Medicine, researchers revealed that the algorithm employs advanced machine learning techniques to analyze high-dimensional imaging data for associations with ischemia progression. This method surpasses the capabilities of human experts by identifying subtle features and patterns in the scans that may go unnoticed.
Expert Insights
Dr. Paul Bentley, study leader at Imperial College London, highlighted the algorithm's advantages: "Machine learning screens for associations that affect lesion anatomy and signal variability, thereby providing more precise assessments. Our approach has proven to be superior to conventional methods for estimating the age of ischemic lesions, making it vital in stroke management."
Importance of Accurate Stroke Timing
Determining the age of brain lesions is crucial, especially when the narrow window for treatment intervention can mean the difference between recovery and lasting damage. However, establishing the exact onset of stroke can be particularly challenging when patients are unable to communicate effectively or lack accompanying individuals to recount the circumstances leading to their symptoms.
Collaborative Research Efforts
In a collaborative effort involving scholars from Imperial College London, the University of Edinburgh, and the Technical University of Munich (TUM), researchers trained a convolutional neural network-radiomics (CNN-R) model to estimate lesion age based on over 800 CT scans with established stroke timelines. When applied to a separate 2,000 CT scans, the model outperformed traditional visual estimation techniques by achieving twice the accuracy.
Biological Age Assessment
This algorithm also assesses the "biological age" of brain damage indicated by CT scans, providing healthcare providers with crucial insights into the severity of the stroke. This additional information can influence treatment decisions regarding potential interventions, particularly in determining which options remain viable based on the time elapsed.
Future Implications
Professor Daniel Rueckert, a recipient of the prestigious Leibniz Prize and an expert in AI and healthcare at TUM, emphasized the model's multifaceted approach: "Our model's strength lies in its ability to analyze the density of the damaged area alongside additional features like texture and variations in the affected regions, leading to more informed medical decisions."
Optimistic Outlook
The research team is optimistic that this model could be implemented in up to 50% of stroke cases in the near future. Dr. Bentley added, "This information will empower doctors to make swift, informed decisions regarding treatment, ensuring the best possible outcomes for stroke patients. With our software being twice as accurate as the current best practice, it has the potential for full automation as soon as a stroke is visible on a scan."
Conclusion
This innovation promises not just enhanced diagnostic accuracy but also a brighter future for stroke patients around the globe. Stay tuned as this technology could soon revolutionize emergency response in stroke care, potentially saving countless lives!
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)