Revolutionary AI-Designed 'Nanocages' Set to Transform Gene Therapy!
2024-12-24
Author: Jia
Groundbreaking Development in Gene Therapy
In a groundbreaking development, researchers have harnessed the power of artificial intelligence (AI) to create a cutting-edge therapeutic platform that replicates the complex structures of viruses. This innovative research, published in the prestigious journal *Nature* on December 18, promises to reshape the landscape of gene therapy.
The Design Inspiration: Viruses
Viruses are nature's masterful designs, adept at encapsulating genetic material within intricate protein shells. This ability not only enables replication but also facilitates the invasion of host cells, often leading to disease. Inspired by their complex structures, scientists have been investigating artificial proteins modeled after these viral specimens, culminating in the creation of novel 'nanocages' that can effectively deliver therapeutic genes to target cells.
Limitations of Existing Nanocages
Despite their promise, existing nanocages have significant limitations; their diminutive size constrains the amount of genetic material they can carry, while their simplistic designs fail to replicate the multifunctionality found in natural viral proteins. Enter the researchers' innovative solution—AI-driven computational design.
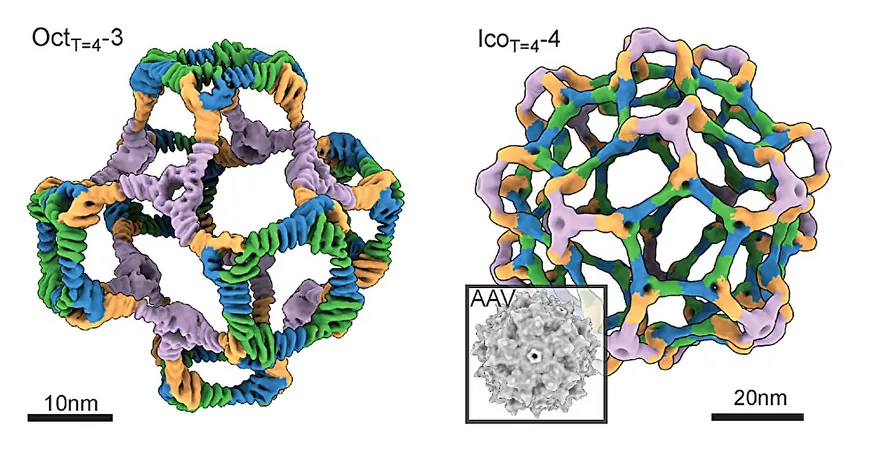
Innovative Solution Through AI
By recognizing that most viruses exhibit symmetrical structures interspersed with subtle asymmetries, the research team leveraged AI to recreate these nuanced characteristics, pioneering the development of nanocages in various geometric forms: tetrahedral, octahedral, and icosahedral.
The icosahedral Nanocages: A Breakthrough
Among their impressive creations, the icosahedral nanocages, with a diameter of up to 75 nanometers, stand out for their capacity to hold three times more genetic material than traditional gene delivery vectors, such as adeno-associated viruses (AAV). This significant increase represents a monumental leap forward in gene therapy possibilities.
Validation Through Testing
Electron microscopy images confirmed that these AI-designed nanocages maintained the precise symmetrical structures as intended. Functional tests demonstrated their efficacy in delivering therapeutic payloads to targeted cells, signaling a promising future for practical medical applications including cancer treatments and genetic disorders.
Expert Opinions
"Advancements in AI have ushered in a new era of tailoring artificial proteins to address critical human health challenges," stated Professor Sangmin Lee, a key member of the research team. "We aspire for this research to not only speed up gene therapy development but also ignite breakthroughs in the next generation of vaccines and other biomedical innovations."
Collaborative Research
This groundbreaking study was conducted in collaboration with the esteemed Professor David Baker, a 2024 Nobel Chemistry Laureate from the University of Washington. Professor Lee highlights the importance of their collaboration, having spent nearly three years under Professor Baker's mentorship before joining POSTECH's Department of Chemical Engineering in early 2024.
Future Implications
As the medical field stands on the brink of a new frontier, this revolutionary research exemplifies how AI could not only redefine gene therapy but also hold the key to advancing a myriad of biomedical innovations that could improve countless lives around the globe. Keep an eye on this developing story; the future of medicine may just be a nanocage away!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)