Revolutionary AI Screening Set to Transform Cardiovascular Disease Detection
2024-10-10
Author: Sarah
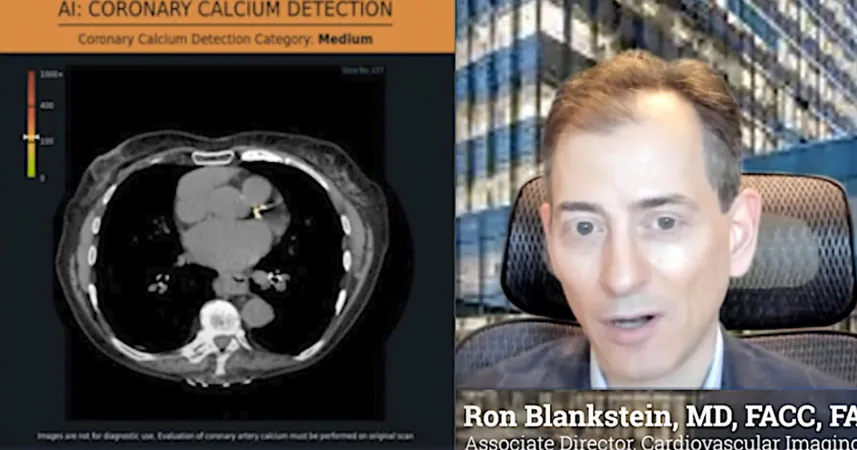
Breakthroughs in artificial intelligence (AI) are dramatically changing the landscape of cardiovascular health, particularly through opportunistic screening using computed tomography (CT) scans. Dr. Blankstein, a leading expert in cardiac imaging, has revealed that AI technology can analyze CT images originally intended for other diagnostic purposes, effectively quantifying calcified plaque in coronary arteries.
Study at SCCT 2024 Meeting
In an impactful study presented at the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography (SCCT) 2024 meeting, Dr. Blankstein collaborated with Dr. Brittany Nicole Weber, director of the Cardio-Rheumatology Clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and the tech company Nanox AI. The research involved analyzing CT scans from approximately 2,500 patients suffering from autoimmune diseases, including lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. Disturbingly, over 50% of these patients showed elevated levels of calcified plaque, significantly heightening their risk for cardiovascular events such as heart attacks.
Link Between Inflammation and Heart Disease
The study underscores the critical link between inflammation—common in those with autoimmune diseases—and heart disease. Inflammation is known to accelerate plaque development, leading to catastrophic health crises like heart attacks when plaques rupture. The findings offer a crucial insight for healthcare providers, enabling them to implement aggressive preventative measures for at-risk patients before they need emergency interventions.
The Role of AI in Early Intervention
AI's role in this screening method presents a groundbreaking opportunity in early cardiovascular disease intervention. "Once we detect calcifications in these patients, we can intensify their treatment, whether it’s lowering LDL cholesterol, optimizing blood pressure, or managing inflammation with medications like colchicine," Dr. Blankstein articulated.
Future of AI in Healthcare
Looking ahead, the potential of AI integration into the healthcare system appears promising. Dr. Blankstein envisions a future where AI flags high-risk patients within electronic medical records (EMR), ensuring that those who may have slipped through the cracks receive timely attention. Experts predict that CT screenings could evolve into a primary prevention tool, allowing for the initiation of treatment years or even decades before any symptoms manifest.
Transforming Preventive Cardiology
Dr. Blankstein emphasized the revolutionizing potential of AI: “The ability to screen millions of chest CTs stored in hospital PACS systems and identify patients with hidden coronary artery disease could redefine preventive cardiology.” By shifting focus from conventional risk factors to actual imaging evidence, health systems can dramatically enhance their population health strategies.
Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
As researchers and healthcare practitioners continue to embrace AI's capabilities, it is poised to enhance diagnostic accuracy and efficiency, leading to timely interventions and improved patient outcomes. Dr. Blankstein noted, "It's not just identifying the disease; it’s about transforming both patient and physician behaviors to minimize risks."
Impact on Cardiovascular Care and Cost
The rising interest in AI-driven opportunistic screening suggests a future where such technologies become integral to cardiovascular care, potentially reducing the global burden of heart disease. Economically, these screenings also promise a cost-effective solution for health systems, allowing for patient assessments without needing dedicated resources. While current reimbursement frameworks do not cover opportunistic AI screening, health systems stand to gain returns on investment through increased patient engagement in cardiology and subsequent treatment pathways.
Conclusion
In this rapidly evolving field, the question remains: will AI screening become the new standard for proactive cardiovascular health? The future of heart health might just hinge on its answer.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)