Revolutionary Airlock Concept Aims to Safeguard Martian Environment During Human Exploration
2024-12-08
Author: Daniel
Introduction
As humanity sets its sights on Mars, preserving the Martian ecosystem from contamination by Earth microbes becomes a critical objective. This is particularly important not only for the integrity of scientific research but also for the future search for extraterrestrial life on the Red Planet.
The Challenge of Current Protocols
While both governmental and commercial space agencies rush to meet ever-ambitious deadlines for manned missions to Mars, current planetary protection protocols are primarily designed for uncrewed missions. This inconsistency raises a significant challenge: how can we ensure the safety of Mars' environment while facilitating human exploration?
The Proposed Airlock Design
A new study addresses this issue by introducing a tailored airlock design intended specifically for enhanced planetary protection. The researchers argue that when astronauts exit their habitats for EVAs (extravehicular activities), they pose the greatest risk of transporting terrestrial microbes onto Mars. Standard airlocks simply do not provide the necessary safeguards against this risk.
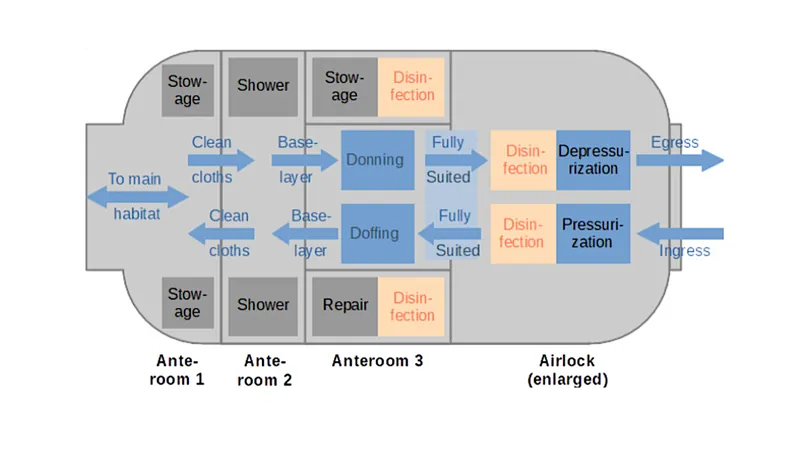
Components of the Airlock
To counter this challenge, the proposed airlock concept incorporates a three-compartment system, ensuring a sterile transition between the interior habitat and the Martian surface. The airlock consists of two sealed doors with an internal area divided as follows:
1. **Suit-Up Area**: This compartment is designated for the preparation and repair of EVA suits, potentially integrating suitports for direct access.
2. **Hygiene Compartment**: Focusing on cleanliness, this zone is equipped with showers and hygiene facilities for astronauts to maintain their health and prevent contamination.
3. **Storage Area**: This section serves as a storage space for undergarments and indoor clothing, further minimizing the chances of carrying Earth-bound microbes outside.
Operational Efficiency and Planetary Protection
The authors of the paper contend that consolidating these vital functions into one airlock module enhances operational efficiency while reinforcing planetary protection protocols. By aligning practical design with mission objectives, the SafeMars concept seeks to ultimately facilitate safer human exploration of Mars.
Conclusion
As humanity prepares for what could be a historic leap into our solar system, adopting innovative solutions like this airlock is essential to avoid jeopardizing the Martian environment. The possibilities are thrilling, but so are the responsibilities that come with them. Will we take the necessary steps to ensure Mars remains a pristine frontier?
For more details about this fascinating development, check the full study published in NPJ Microgravity on October 7, 2023.
Stay tuned as we continue to explore the advancements of human space exploration!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)