Revolutionary DNA-Based Storage Technology Transforms Brain MRI Data Management!
2024-09-29
Author: Li
Introduction
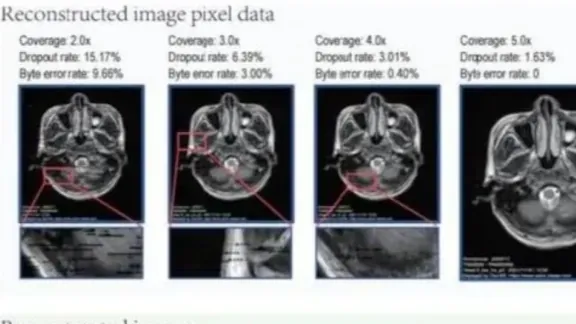
In a groundbreaking advancement for medical data storage, researchers from Tianjin University's Frontiers Science Center for Synthetic Biology, teaming up with Tianjin Huanhu Hospital, have introduced the revolutionary DNA Palette coding scheme. This innovation allows brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data to be encoded into DNA, facilitating lossless decoding and enabling the three-dimensional reconstruction of complex imaging data.
Significance of the Research
Published in the prestigious journal National Science Review, this research could reshape how we manage the vast amounts of data generated by brain MRI scans—a crucial tool in diagnosing conditions, planning surgeries, and assessing treatment efficacy.
Challenges with Traditional Storage
Traditionally, the monumental data output from brain scans has posed severe challenges for long-term storage solutions, hampering progress in managing chronic neurological disorders like juvenile Parkinson’s, epilepsy, and various neurogenetic conditions. These illnesses necessitate the continuous accumulation and analysis of patient data over a lifetime. Current storage mediums often fail to meet the demands of such extensive data needs.
The Innovation of DNA Storage
Enter DNA—a remarkable biological molecule known for its incredible stability and storage density. The Tianjin research team achieved a stunning feat, encoding over 11.28 megabytes of brain MRI data into around 250,000 DNA sequences. This incredible achievement resulted in an impressive data density of 2.39 bits per base, showcasing DNA’s capabilities in vibrant detail.
Storage and Retrieval
Once encoded, the synthetic DNA oligos are stored in a lightweight dry powder form, weighing as little as 3 micrograms. Remarkably, this invention can support over 300 read operations under current technological standards, pointing to DNA's tremendous potential as a secure and efficient long-term data storage medium.
Future Prospects
This major milestone highlights the prospect of practical applications of DNA data storage in the medical field, offering a robust solution for the secure management of vast quantities of medical information. With the accelerated push towards adopting DNA-based storage technologies, the future of medical data management looks promising, potentially revolutionizing how we store and access critical health information.
Conclusion
Stay tuned as this technology unfolds—could DNA be the answer to our data storage dilemmas?




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)