Revolutionary Extraction Method Uses Liquefied Dimethyl Ether to Harness Premium Rice Bran Oil
2024-10-07
Author: Mei
Introduction
As the world grapples with increasing demand for high-quality, sustainable oils, rice bran oil is gaining traction due to its impressive content of γ-oryzanol, a compound known for its numerous health benefits. However, conventional extraction methods utilize hexane, a process that raises significant environmental concerns due to the solvent's toxicity and adverse ecological effects.
Groundbreaking Research
In a groundbreaking study by researchers at Chulalongkorn University, liquefied dimethyl ether (LDME) has emerged as a superior alternative for extracting rice bran oil. This innovative approach promises to not only uphold the quality of the oil but also to align with sustainability efforts, thereby ticking all the right boxes for eco-conscious consumers.
Key Findings
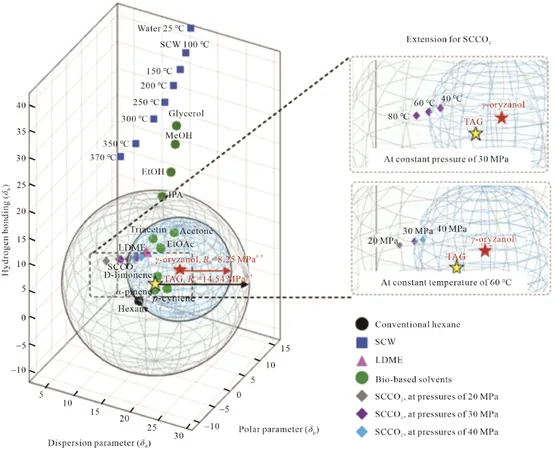
The comprehensive research, shared in the Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts, meticulously compared LDME to hexane by assessing its solubility, extraction efficiency, and the quality of the oil produced. Astonishingly, the results revealed that LDME outperformed hexane, significantly reducing solvent requirements, shortening extraction times, and operating effectively at lower pressures.
Expert Insights
Lead researcher Phannipha Daisuk stated, "Our research demonstrates that LDME can effectively replace hexane, offering a safer and more environmentally friendly option for extracting rice bran oil." Additionally, the study confirmed that the extraction process using LDME did not compromise the protein and carbohydrate structures of rice bran, thus ensuring the sustainability of its by-products.
Comparison with Supercritical Carbon Dioxide
Moreover, the research also evaluated LDME against supercritical carbon dioxide (SCCO2), another potential alternative for oil extraction. While SCCO2 displayed some promising results, it demanded higher ratios of solvent to rice bran and the use of co-solvents to attain similar extraction rates. This not only raises questions about its economic viability but also makes LDME the more attractive option for industries aiming for sustainability without compromising efficiency.
Conclusion and Future Prospects
This groundbreaking discovery marks a pivotal advancement in sustainable extraction of rice bran oil, catapulting LDME into the spotlight as a game-changer in the industry. As the research team looks ahead, their focus will shift toward scaling up the extraction process and performing detailed techno-economic and environmental impact assessments.
In an era where eco-friendliness is becoming paramount, this research not only reshapes the way rice bran oil is produced but could also set a precedent for sustainable practices in the broader oil extraction industry. Stay tuned as we explore the implications of this innovative method in the coming months!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)