
Revolutionary Findings in Mammalian Evolution: Are We Underestimating Our Ancestors?
2024-10-03
Author: Li
Introduction
In a groundbreaking revelation for paleontology enthusiasts, researchers have unearthed new evidence that reshapes our understanding of mammalian evolution, particularly concerning their jaw structure. This discovery, linked to two ancient mammal precursors, promises to fill significant gaps in our knowledge about how modern mammals came to be.
Focus of the Study
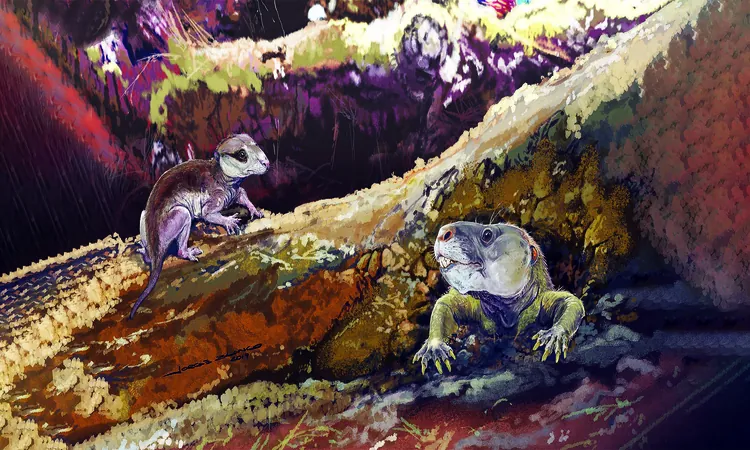
The focus of this eye-opening study revolves around two fossils from species known as Brasilodon quadrangularis and Riograndia guaibensis. These findings act as crucial windows into the evolutionary journey of mammal jaw functionality and the development of the middle ear, suggesting that the evolutionary processes were far more adventurous than previously assumed.
Jaw Structures in Mammals
Mammals are uniquely characterized by their specialized jaw structure, which is complemented by three bones in the middle ear—a significant leap from their earlier vertebrate ancestors, which possessed only one middle ear bone. The fossilized remains of cynodonts, ancestors to modern mammals, have long intrigued scientists as they represent a transitional phase in this evolutionary marvel.
New Insights Through Technology
Thanks to advanced imaging technology, particularly CT scanning, researchers were able to digitally reconstruct the jaw joints of these ancient cynodonts. This analysis revealed a ‘mammalian-style’ connection between the skull and the lower jaw in Riograndia guaibensis—17 million years earlier than the earliest known specimen that exhibits this type of development.
Significance of Findings
It's important to note that Brasilodon quadrangularis, which is more closely related to present-day mammals, did not demonstrate this feature. What does this mean? It indicates that the evolution of jaw functionality may have taken several paths within different lineages, thereby suggesting that traits we consider unique to mammals might have evolved multiple times independently.
Expert Commentary
James Rawson, a key figure in this study and part of Bristol's School of Earth Sciences, noted, “The acquisition of the mammalian jaw contact was a key moment in mammal evolution. This research illustrates that a variety of cynodont groups were experimenting with different jaw joint types, leading to the emergence of characteristics we once presumed were exclusive to mammals.”
Implications of the Study
The implications of these findings extend far beyond academic interest. They provide a fresh perspective on how structural elements like the mammalian jaw joint and middle ear bones evolved through a mosaic pattern across various cynodont groups. Dr. Agustín Martinelli from the Museo Argentino de Ciencias Natural pointed out that these Brazilian fossils are unveiling a rich trove of information that will enhance our understanding of mammalian origin.
Fossils as Historical Archives
Fossils serve as vital historical archives that offer crucial insights into the evolutionary tapestry of life on Earth. The discoveries related to Brasilodon quadrangularis and Riograndia guaibensis represent pivotal moments in the evolutionary narrative—highlighting not only the structural adaptations over time but also the different evolutionary paths taken by various lineages.
Future Research Prospects
Looking toward the future, the prospects for paleontological research are brimming with possibilities. Scientists are gearing up to examine more fossil sites in South America, which are considered treasure troves for ancient mammalian evidence. Professor Marina Soares of the Museu Nacional in Brazil emphasized the region's unparalleled diversity of cynodont forms, calling for further exploration to enhance our understanding of early jaw joint functionality.
Closing Remarks
The study is a clarion call for collaborative efforts among paleontologists, biologists, and technologists, all striving to delve deeper into life's ancient mysteries. As research continues, we may discover even more transformative truths about our mammalian ancestors and the complex narratives that define our evolutionary history. With every new finding, the world of mammalogy stands poised on the brink of exciting revelations.
Publication
This remarkable study has been published in the prestigious journal *Nature*, underscoring the importance of these discoveries.
Stay Tuned
Stay tuned for more riveting discoveries in our ongoing journey to understand our roots in the animal kingdom!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)