Revolutionary Findings on Extracellular Vesicles Could Bring Hope to Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients
2024-11-20
Author: Wei
Introduction
In a groundbreaking study, researchers from the Germans Trias i Pujol Research Institute (IGTP) and the Institut d'Investigació Sanitària Pere Virgili (IISPV) have unveiled promising insights into the therapeutic potential of extracellular vesicles (EVs) in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). This innovative approach could soon reshape the landscape of treatment options for millions suffering from this debilitating condition.
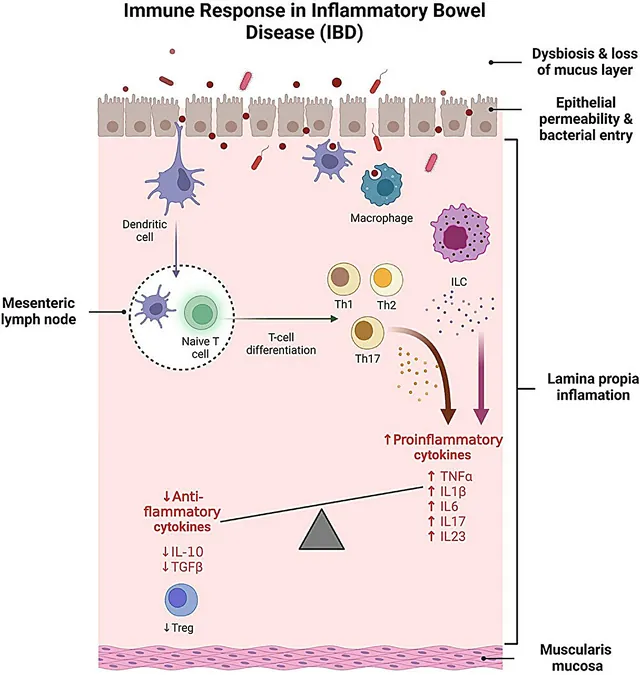
What is Inflammatory Bowel Disease?
Inflammatory bowel disease, which includes Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, wreaks havoc on the gastrointestinal tract due to chronic inflammation and an unbalanced immune response. Unfortunately, despite advancements in treatment over recent years, nearly 50% of patients may still require surgical intervention within a decade of diagnosis, underscoring the urgent need for more effective therapies.
Collaboration and Findings
The collaborative effort between the Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Research Group (GReMII) at IGTP, the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Research Group (IBODI) at IISPV, the Universitat Rovira i Virgili (URV), and the CIBER of Hepatic and Digestive Diseases (CIBEREHD) has yielded pivotal findings published in the esteemed journal Clinical and Translational Medicine.
The Promise of MSC-EVs
Dr. Josep Manyé, a key researcher in the study, highlighted the advantages of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles (MSC-EVs) over traditional cellular therapies. "MSC-EVs represent a promising therapeutic alternative, offering significantly lower risks associated with immunogenicity and tumorigenicity,” he noted, emphasizing their ease of storage and handling.
Beneficial Properties of MSC-EVs
The review meticulously investigates the various beneficial properties of MSC-EVs, such as their immunomodulatory, pro-regenerative, anti-apoptotic, and anti-fibrotic capacities - all of which have shown promise in preclinical studies. Dr. Carolina Serena, another co-author and principal investigator at IISPV, stressed the importance of advanced techniques, including transcriptomics, proteomics, and lipidomics, in understanding MSC-EVs and their potential to restore intestinal balance.
Challenges and Future Research
One of the most exciting aspects of this research is the comprehensive exploration of MSC-EVs’ characterization and isolation methods, while also addressing the obstacles in translating this therapeutic promise into clinical practice. Dr. Laura Clua-Ferré, the first author, pointed out that the findings lay a solid groundwork for future research aimed at developing safer and more effective IBD therapies.
Current Clinical Trials
This research is particularly timely, as around 20 phase I and II clinical trials are currently underway, investigating the application of EVs for various conditions. However, the authors caution about the regulatory and logistical challenges that must be navigated before these therapies can be made available to patients.
Conclusion
Could MSC-EVs be the game-changer that IBD patients have been waiting for? As researchers continue to unravel the mystery of these tiny yet powerful vesicles, we may soon witness a revolution in how chronic inflammation is treated, paving the way for healthier lives and renewed hope for those afflicted by inflammatory bowel disease. Stay tuned as this thrilling research progresses!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)