Revolutionary 'Microjet' Technology Set to Replace Needle Injections!
2024-11-22
Author: Ming
Introduction
In a groundbreaking study published in *Nature*, researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Novo Nordisk have developed innovative devices inspired by the unique mechanisms of cephalopods. These "microjet" systems aim to significantly reduce or even eliminate the need for needle injections in administering medications, marking a monumental shift in how patients receive treatments.
How It Works
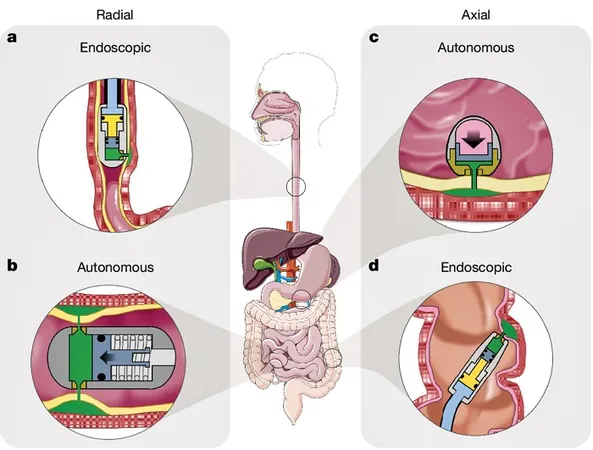
Imagine using a device that ejects a high-velocity stream, like a water flosser puncturing a balloon, this ingenious technology penetrates gastrointestinal tissue without the discomfort associated with needles. The research team is focusing on two versions of the microjet device: one that can be used in clinical settings and another designed to be ingested for at-home use.
Advantages of Microjet Technology
Small, swallowable devices have been around for some time, but what sets these apart is their advanced needle-free delivery mechanism. Giovanni Traverso, a lead author of the study, emphasizes that "the potential to reduce or eliminate needles could greatly enhance the safety and user-friendliness of medical treatments." This is crucial because needle delivery often requires specialized training and comes with strict disposal protocols, adding to the anxiety for many patients.
Design and Precision
The design and functionality of these microjets mimic the natural abilities of cephalopods to control the direction of their jet propulsion, making them ideal for targeting either narrow tubes like the esophagus or larger areas such as the stomach. This directional precision ensures that the medication is effectively delivered into the desired tissue layers rather than being wasted in the body’s lumen. Impressively, the ingestible devices are comparable in size to a size 000 pill capsule, measuring 26.1 mm in length.
Test Results
In tests conducted on ex vivo tissues, the microjet devices were dramatically effective in delivering essential medications like insulin, GLP-1 analogs, and siRNA, matching results seen with traditional injections. Further trials in living pigs and dogs produced similar outcomes, showcasing the technology's significant potential.
Challenges Ahead
However, challenges remain before these devices can be used safely by patients. Notably, the team did not test whether the ingestible devices could be swallowed safely, as they were directly introduced into the stomach and intestines during trials. Niren Murthy, a bioengineering professor at the University of California, Berkeley, who was not involved in the study, suggests that a critical next step will be ensuring the capsules are pH-sensitive, allowing for controlled release of their payloads. If these capsules are ingested, it’s essential they do not release their contents while still in the stomach but rather wait until they reach the small intestine.
Conclusion
This innovative advancement has the potential to revolutionize the healthcare landscape, making medical treatments less invasive, more comfortable, and significantly more accessible. Imagine a future where managing chronic diseases is as easy as swallowing a pill! The journey to widespread implementation may be complex, but the promise of needle-free medicine is finally within reach. Stay tuned for more updates on this exciting technological leap!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)