Revolutionary Nanoparticle Therapy May Hold the Key to Combat Obesity by Targeting Fat Absorption!
2024-10-13
Author: Wei
Overview
In an exciting development in the fight against obesity, researchers have unveiled a groundbreaking nanoparticle therapy aimed specifically at reducing fat absorption within the small intestine. This innovative approach, detailed in the prestigious journal Advanced Science, has shown remarkable promise for preventing diet-induced obesity.
Targeting SOAT2
Presented at the highly-regarded UEG Week 2024, the study centers around a critical enzyme known as Sterol O-acyltransferase 2 (SOAT2). This enzyme is instrumental in the body’s fat absorption process. By inhibiting SOAT2 directly in the small intestine, the researchers suggest a powerful new therapeutic pathway that could vastly reduce fat absorption and stave off obesity.
Research Insights
Dr. Wentao Shao, the lead researcher of the project, explained, “For years, we have focused on fat metabolism in our research. However, finding effective means to block fat absorption has been a significant challenge.” Unlike traditional approaches that concentrate on reducing dietary fat intake, this novel strategy targets the very mechanism of fat absorption itself.
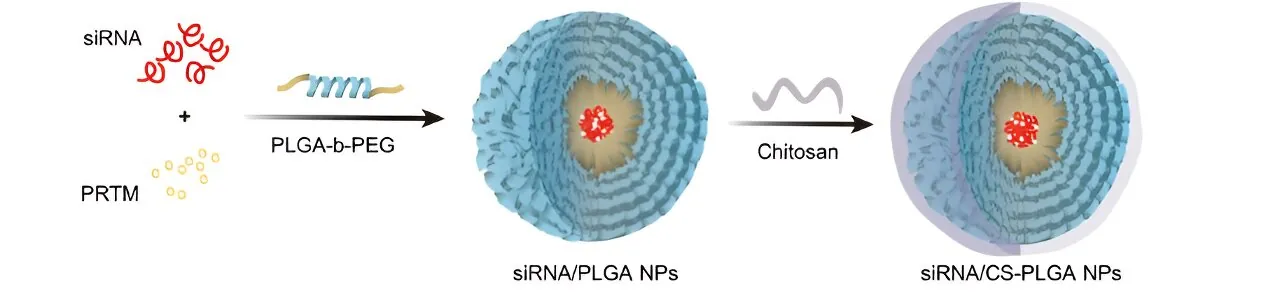
Nanoparticle Mechanism
The research team crafted a sophisticated delivery mechanism utilizing nanoparticles—a minuscule capsule consisting of a polymer core encased in a protective outer shell. This system is engineered to transport small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) directly to the small intestine, where they can effectively diminish SOAT2 expression and impede fat absorption. In tests conducted on mice, it was observed that those receiving the nanoparticle therapy absorbed significantly less fat and managed to avoid obesity, even when consuming a high-fat diet.
Advantages of the Therapy
"This oral treatment offers multiple advantages," Dr. Shao highlighted. “It is non-invasive, has low toxicity, and could potentially improve patient adherence as compared to current obesity treatments, which often require more invasive procedures or are challenging to maintain.” These attributes position this new therapy as a promising alternative in obesity management.
Understanding SOAT2's Role
Moreover, the study elucidates how SOAT2 regulates fat absorption. When SOAT2 is inhibited in the gut, it stimulates the degradation of CD36—a protein crucial for fat transportation. This process involves both cellular stress responses and the action of E3 ligase RNF5, an enzyme that promotes CD36 breakdown.
Comparative Safety
Significantly, previous research indicated that blocking SOAT2 in the liver can lead to unwanted fat accumulation within that organ, whereas this intestinal-focused approach minimizes that risk. “One of the most thrilling aspects of our therapy is its capability to zero in on fat absorption in the intestine while leaving the liver untouched,” commented Professor Zhaoyan Jiang, who supervised the study. “This is crucial because past studies have shown the fat buildup risk associated with hepatic SOAT2 blocking, a danger our treatment method cleverly sidesteps.”
Future Directions
Looking to the future, the research team is eager to test their nanoparticle system in larger animal models to validate its efficacy and safety for human applications. "We firmly believe that this revolutionary nanoparticle system marks a significant advancement in obesity management," Professor Jiang asserted. "It could herald a new era of effective treatments that directly address fat metabolism and diet-related weight gain."
Conclusion
Could this breakthrough therapy be the game-changer we've been waiting for in the battle against obesity? Stay tuned as researchers continue this promising line of investigation!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)