Revolutionary Nanoparticles Set to Transform Stem Cell Treatments Inside the Body!
2024-12-23
Author: Wei
Revolutionary Nanoparticles Set to Transform Stem Cell Treatments Inside the Body!
In a groundbreaking development in medical science, researchers at Georgia Tech, Emory University, and the University of California, Davis, have unveiled a novel technique involving nanoparticles that could democratize stem cell therapies and make them far more accessible to patients battling severe blood disorders and genetic conditions. This innovative approach could not only reduce the risks associated with current treatments but also streamline the entire process significantly.
The Challenge with Traditional Stem Cell Treatments
Currently, hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) therapies are often invasive and complex, requiring the extraction of stem cells from a patient's bone marrow. Patients typically have to undergo chemotherapy to prepare their bodies for the modified cells, a process that can be painful and life-threatening. James Dahlman, McCamish Early Career Professor at Georgia Tech's Wallace H. Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering, tells us, "These therapies are effective but also hard on the patients. Our aim is to simplify this. Instead of subjecting patients to invasive procedures, we envision using an IV drip to administer treatment."
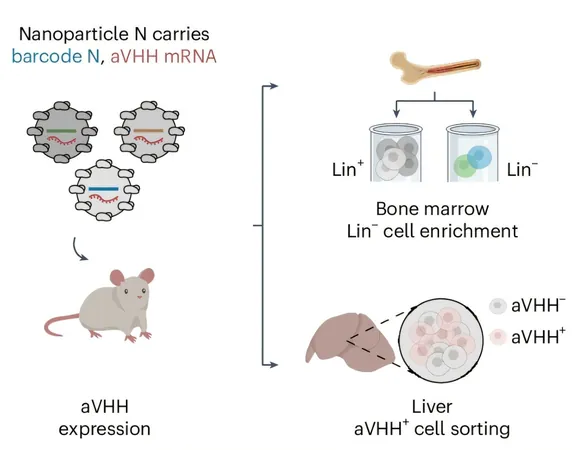
Enter the Game-Changer: LNP67 Nanoparticle
Dahlman and his team have developed a specific nanoparticle called LNP67, which eliminates the need for complex targeting ligands typically required to deliver genetic instructions effectively. "This nanoparticle is chemically simple, making it easier to manufacture and potentially scalable like mRNA vaccines," Dahlman explains. The breakthrough lies in LNP67's unique ability to navigate the body’s defenses, particularly the liver, which is often overly efficient at filtering out foreign substances and medications.
Stealth Delivery: How LNP67 Outsmarts the Liver
The liver plays a crucial role in metabolizing substances in the bloodstream, which can be a hurdle in delivering vital therapeutic agents. By ingeniously designing the LNP67 to avoid detection by liver mechanisms, the researchers have managed to enhance delivery efficiency to other tissues significantly. "Even a 10 percent improvement in avoiding liver capture can double the nanoparticles' delivery to target cells," Dahlman asserts.
A Potential Leap in Treating Blood Disorders
This novel approach can drastically alter the landscape of treating genetic blood diseases, such as sickle cell anemia and various immune deficiencies. The potential for reduced discomfort and lower risk, combined with a simple IV administration, marks a significant step forward for patient care in this arena.
The research team performed extensive testing on 128 unique nanoparticles, eventually identifying 105 candidates without the need for additional targeting ligands. The final product, LNP67, excelled in safely and effectively delivering mRNA payloads to HSCs, demonstrating the viability of simpler, less intrusive stem cell therapies.
What Lies Ahead?
The implications of this revolutionary research extend far beyond hematopoietic stem cells. The success of the LNP67 nanoparticle opens doors to broader applications in genetic therapies and regenerative medicine, shifting the paradigm towards more patient-friendly treatment options that are both effective and less invasive.
As the medical community eagerly anticipates further developments, this innovative breakthrough serves as a beacon of hope for countless patients in need of effective and less arduous therapeutic alternatives. Stay tuned for more updates on this remarkable story in stem cell innovation!





 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)