Revolutionary Robotic "Convoy" Set to Transform Endoscopic Surgery
2024-10-02
In a groundbreaking advancement for medical technology, a team of researchers led by Tian Qiu at the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) in Dresden has successfully developed a solution designed to enhance endoscopic surgery. The current generation of miniature robots, while promising, faces significant limitations in mobility and weight-bearing capacity. These tiny robots often struggle to maneuver across slippery, mucus-covered surfaces within the human body, limiting their effectiveness during critical surgical procedures.
Introducing the TrainBot
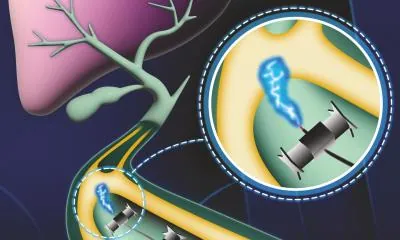
Enter the innovative "TrainBot," a revolutionary system that connects multiple millimeter-scale robots. Equipped with advanced anti-slip feet, this robotic convoy can efficiently transport endoscopic instruments, overcoming the traditional challenges faced by singular units. The TrainBot operates wirelessly, utilizing a rotating magnetic field to control the movement and rotation of each individual unit. This external actuation and control system is specifically designed to navigate the complex inner landscapes of the human body.
Published Findings and Optimism
The team's findings are published in the prestigious journal *Advanced Science*, marking a significant step forward in endoscopic technology. "After the promising results with the TrainBots in our simulations using an organ model, we are optimistic about the potential for this technology to revolutionize endoscopic surgery," stated Moonkwang Jeong, lead author and a key member of the research team.
Simulated Surgical Procedures
One of the most compelling applications of the TrainBot system was demonstrated during a simulated surgical procedure involving bile duct cancer. In cases where the bile duct becomes obstructed—a dangerous condition leading to bile buildup—surgical intervention is critical. The robotic convoy adeptly navigated through challenging angles within the body to maneuver an endoscopic instrument for a process known as electrical tissue ablation. During this intricate procedure, a wire electrode, measuring 25 cm in length and weighing significantly more than a single TrainBot unit, was guided to the blockage site. Once in position, electrical voltage was applied, leading to a gradual and precise removal of the tissue obstruction through electrocauterization.
Future Potential of TrainBot
Future enhancements to this technology could see TrainBot convoys performing a variety of tasks, such as delivering catheters for fluid drainage or administering medications. "Our work paves the way for developing teams of miniature robots that could tackle a wide range of challenges in endoscopic surgery," Jeong noted.
Conclusion
As the field of robotic surgery continues to evolve, advancements like the TrainBot could not only lead to safer surgical outcomes but also push the boundaries of what is possible in minimally invasive procedures. This innovation could soon change the landscape of medical treatment, offering hope for patients facing complex surgeries in the near future.





 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)