
Revolutionary Rover Protocol Promises Breakthroughs in Extraterrestrial Life Detection!
2024-11-18
Author: Arjun
In the quest to uncover evidence of life beyond Earth, scientists are faced with the daunting task of exploring whether life exists, has existed, or has never existed on other planets. This mission is intricate and hinges on a series of sophisticated experimental studies designed to identify various life signatures, each of which presents its own unique challenges.
One of the fundamental hurdles in extraterrestrial research is the limitation imposed by time, resources, and mobility. As a result, the need for precise and unequivocal research methodologies becomes paramount. Addressing this challenge, recent research has introduced an innovative protocol for life detection that maximizes efficiency while delivering reliable outcomes based on empirical data gathered through chemical analyses.
Unlike conventional approaches that primarily focus on biomolecules, this study aims for minimal operational costs and reduced complexity in mission execution. By integrating multiple biomolecular detection techniques into a cohesive framework, the researchers enhance overall mission performance, all while respecting time and resource constraints.
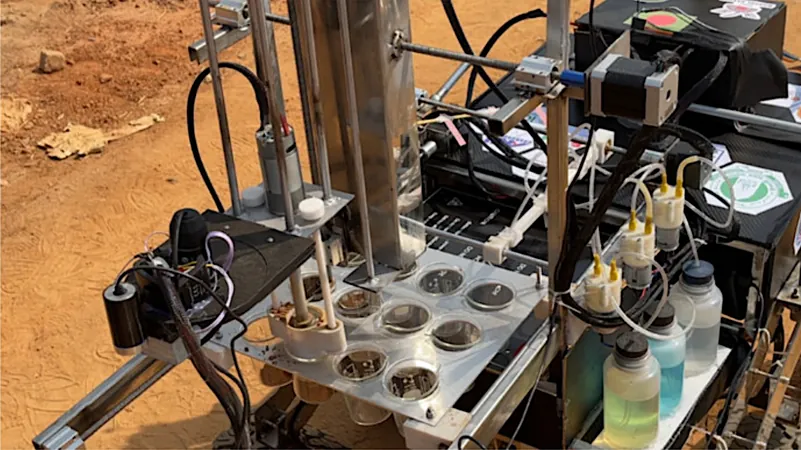
In a groundbreaking study published in *Scientific Reports*, a new rapid multiple biomolecules-based life detection protocol (MBLDP-R) has been developed and incorporated within an operational scientific rover subsystem, specially designed for planetary analysis missions. Utilizing artificial biomolecule samples and simulated extraterrestrial environments, the protocol showcases its capabilities for in-situ analysis and decision-making.
Key biomolecules identified in the study include lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, ammonia, and pigments. A rigorous qualitative test scoring methodology helps rank these biomolecules to identify the most effective detection methods for the final selection.
The rover’s scientific subsystem employs this robust protocol to conduct onboard analysis of soil samples. Evaluation results reveal impressive metrics:
1. The MBLDP-R protocol boasts an average F1-score of 98.65% (macro) and 90.00% (micro) for accurately predicting life classes.
2. The area under the Receiver Operating Characteristics (AUC-ROC) curve confirms the predictive success rate, correctly categorizing samples 92% of the time, including a remarkable 97% accuracy for detecting extant life.
3. With an average completion time of just 17.60 minutes, the protocol is designed for rapid detection of biosignatures, which could significantly expedite astrobiology missions.
This pioneering research not only provides critical insights for future studies focused on astrobiology but also establishes a vital reference for developing scientific frameworks that meet specific mission requirements under resource constraints.
With the advent of such efficient detection protocols embedded in rovers, the possibility of unveiling the mysteries of extraterrestrial life is more tangible than ever. Prepare for the age of discovery as we push the boundaries of our understanding of life beyond Earth!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)