Revolutionary Software Transforms Gene Expression Mapping with 3D Precision!
2025-03-26
Author: John Tan
In a groundbreaking development, researchers at the University of Tsukuba have unveiled "tomoseqr," a cutting-edge software tool that simplifies the estimation of three-dimensional (3D) spatial distribution of gene expression. This free-to-use software has been integrated into Bioconductor, a renowned international platform dedicated to life science software. This innovative tool aims to empower researchers in their quest to decode the complex roles of genes in organism development, disease mechanisms, and regenerative biology. The significant findings of this study have been published in the reputable journal PLOS ONE.
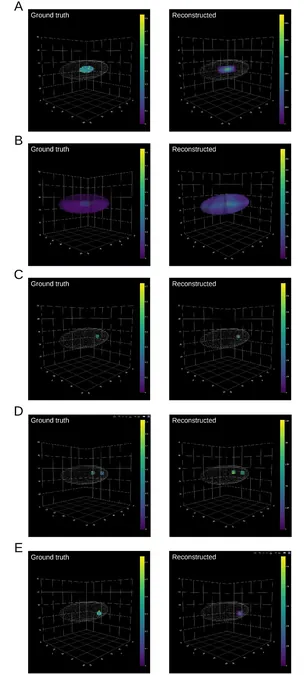
Understanding the 3D spatial organization of gene expression—which reveals where a gene is active or inactive within biological tissues—is crucial for elucidating gene functions. Traditional methods, such as RNA tomography, involve meticulous processes including the preparation of frozen tissue sections along three orthogonal axes, followed by RNA sequencing on each section, which is then compiled into a comprehensive 3D gene expression map. Unfortunately, these methods often require advanced programming skills, posing challenges for researchers lacking computational expertise.
Enter tomoseqr, a user-friendly software that eliminates many of these barriers. With its intuitive graphical user interface, tomoseqr streamlines the creation of tissue morphology data and allows scientists to visualize intricate 3D gene expression models effortlessly. This tool democratizes access to complex analyses, extending its capabilities to a wider research community, including those who may not have extensive computational backgrounds.
In exciting applications of the software, researchers successfully leveraged tomoseqr to analyze gene expression data from zebrafish, leading to the accurate reproduction of known gene expression patterns—solidifying the software's reliability and utility. Furthermore, they explored the gene expression of roughly 18,000 genes in planarians, a fascinating model organism celebrated for its remarkable regenerative capabilities. By mapping the 3D spatial distribution of gene expression, the research revealed significant spatial fluctuations in several genes, hinting at their potential involvement in vital biological functions such as tissue regeneration.
As the scientific community anticipates further advancements in genomics and regenerative medicine, tomoseqr stands out as a powerful ally for researchers, promoting a deeper understanding of the genetic foundations that underlie life processes. With this tool at their fingertips, the possibilities for discovery in fields ranging from developmental biology to therapeutic interventions are truly limitless!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)