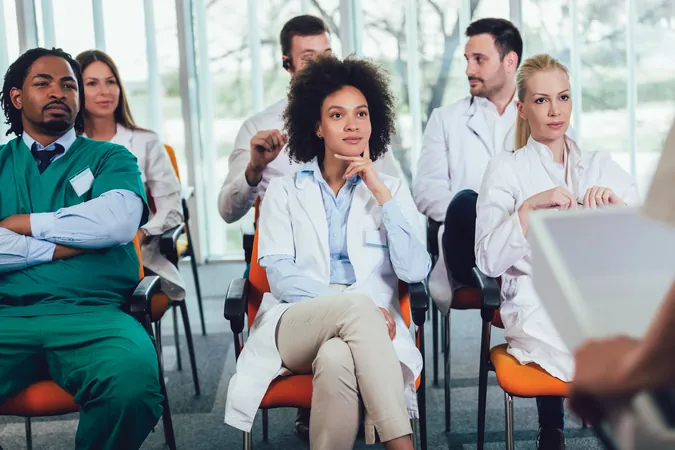

Revolutionary Training Boosts Maternal Cardiac Arrest Management: What You Need to Know!
2024-11-19
Author: John Tan
Introduction
Recent research published in JAMA Network Open reveals that Obstetric Life Support (OBLS) training dramatically enhances the management of maternal cardiac arrest (MCA) among healthcare providers. This groundbreaking study highlights the importance of specialized training in improving the survival rates of mothers experiencing cardiac arrest during childbirth, a rare but critical situation that affects approximately 1 in 3,885 women admitted for delivery.
Current Survival Rates and Challenges
In the United States, MCA currently has a survival rate of only 16%, yet this figure stands to improve dramatically. The American Heart Association suggests that enhancing the “chain of survival” through better training is essential in reducing the significant maternal mortality rate of 22.3 deaths per 100,000 live births. Alarmingly, there are no specific training requirements for managing MCA in the U.S. healthcare system.
The OBLS Program
The OBLS program was meticulously designed to equip healthcare professionals with vital skills in MCA management, focusing on evidence-based practices. The study involved a randomized clinical trial where participants, all English-speaking healthcare providers aged 18 and over, underwent either OBLS education or no training at all.
Study Design and Findings
Participants were randomly assigned to two groups: one receiving comprehensive OBLS education designed to simulate real-life scenarios and the other serving as a control group. Evaluations were conducted at multiple intervals: at enrollment, after the intervention, and six and twelve months later. The study focused on assessing cognitive knowledge and confidence among healthcare providers.
Notably, out of the 46 healthcare professionals analyzed, comprising diverse ethnic backgrounds (58% White, 7% Asian, 7% Black, 2% Hispanic, and 2% other), only 37% had prior experience as simulation instructors. What’s remarkable is that the intervention group showcased significant improvements in both cognitive and megacode scores, with averages soaring to 79.5% and 91%, compared to 63.4% and 61% in the control group, respectively.
Furthermore, the OBLS-trained group boasted an impressive pass rate of 90%, while the control group's success rate was a mere 10%. Confidence levels also saw a marked increase; OBLS participants scored an average of 17.9 on confidence assessments, compared to just 13.3 for those without training. The control group did show some growth in confidence after receiving OBLS education later on, but this highlights the immediate benefits of the training.
Conclusion and Future Steps
Given these promising results, the researchers strongly advocate for the broader implementation of resuscitation training programs across hospitals. They argue that enhancing healthcare professionals' readiness to handle maternal medical emergencies could play a vital role in saving lives.
As the medical community continues to address maternal health challenges, this research underscores an urgent need to prioritize advanced training programs like OBLS to improve outcomes for mothers and their newborns. Will your hospital be next to adopt this life-saving training? Don't miss the chance to be part of this crucial movement in maternal health!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)