Revolutionizing Skincare: How Self-Assembling Proteins are Set to Transform the Industry
2024-11-20
Author: Jia
If you’re passionate about skincare, you might have noticed the booming Personal Skincare Products (PSCPs) industry, projected to hit a staggering $74.12 billion by 2027 with an impressive annual growth rate of 8.64%. In this fiercely competitive landscape, companies are on a relentless pursuit to innovate, striving to create products that deliver superior performance while addressing growing consumer demands for sustainability.
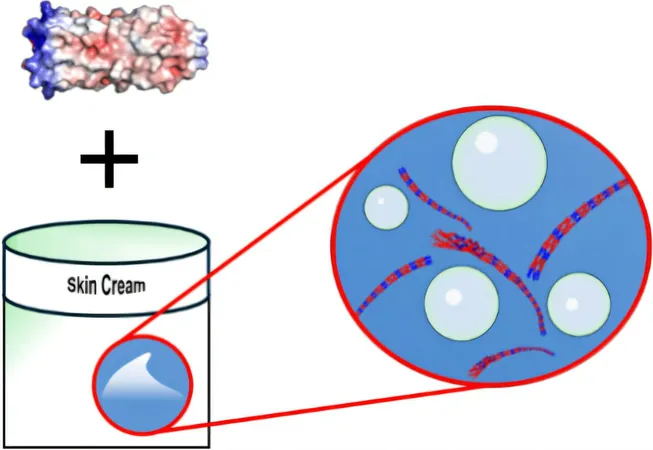
A groundbreaking study led by Professor Jin Kim Montclare and her team at the lab of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has unveiled an exciting innovation—a novel protein-based gel named Q5. This new ingredient represents a significant leap forward for eco-conscious skincare enthusiasts seeking high-performance products that also prioritize environmental responsibility.
Q5 is not just a typical gel; it has the potential to revolutionize the rheological (flow-related) properties of skincare formulations. Its impressive pH stability makes it perfectly suited for the slightly acidic environment of human skin, ensuring that products remain effective and safe for use. This could streamline the formulation process for creating eco-friendly skincare items, increasing their efficacy and durability while aligning with ethical sourcing practices, which are increasingly important to consumers today.
From luxurious beauty creams to essential medical ointments, skincare products commonly depend on intricate "chassis" formulations—most often emulsions or gels—to effectively deliver their active ingredients. The efficacy of these products is significantly influenced by the stability of these formulations, especially under varying environmental conditions such as pH levels.
Traditionally, the skincare industry has leaned on polysaccharides and synthetic polymers to achieve the desired consistency and stability. However, these substances often raise sustainability concerns, especially regarding their sourcing and environmental impact. Enter Q5: Montclare and her team engineered this self-assembling coiled-coil protein to address these pressing issues. Q5’s unique structure allows it to form exceptionally strong gels that resist degradation in acidic environments, suggesting a remarkable advancement in the longevity and performance of skincare products.
By cultivating Q5 through sustainable bacterial or yeast fermentation processes, the researchers are circumventing ethical dilemmas and ecological consequences associated with animal-derived proteins and traditional synthetic polymers. Additionally, Q5's natural ability to attract and retain moisture makes it a versatile ingredient, able to bind a variety of molecules while also functioning as an effective moisturizer.
As the skincare market continues to thrive, innovations like Q5 could not only reshape product formulations but also set new standards for sustainability and ethical production in the beauty industry. Consumers are increasingly looking for products that not only work well but also reflect their values, and Q5 may just be the game-changer that meets those expectations!
Stay tuned as we continue to follow this exciting development in skincare science, paving the way for more sustainable and high-performance products that care for both skin and the planet.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)