
Shocking Antarctic Sea Ice Melting Sparks Surge in Ocean Storms!
2024-12-18
Author: Yu
Groundbreaking Study Uncovers Link Between Sea Ice Melting and Storm Activity
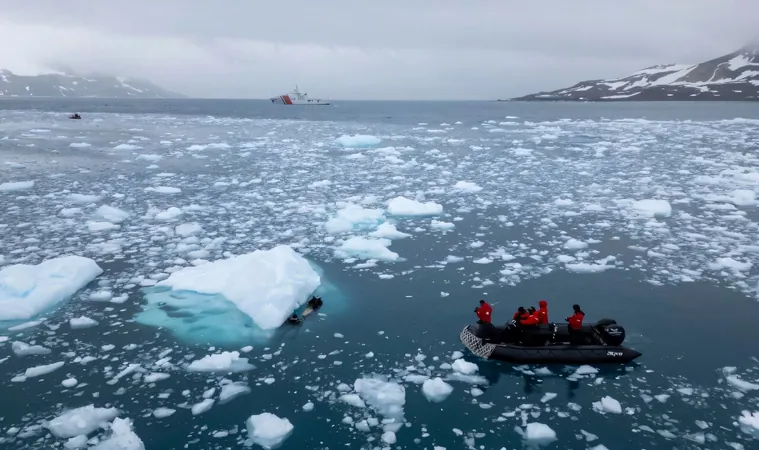
In a groundbreaking study published in the esteemed journal Nature, scientists have uncovered alarming evidence linking the unprecedented retreat of Antarctic sea ice in 2023 to an uptick in storm activity over the Southern Ocean. This dramatic shift may have severe implications for our climate and ecosystems!
A Record Decline in Antarctic Sea Ice
The last several years have seen a significant decline in Antarctic sea ice since 2016, but 2023 set a chilling new record with an incredible amount of ice failing to reform during the winter. Experts warn that this loss doesn't just threaten adorable penguin populations and contribute to the melting of ice shelves. It may also destabilize our atmosphere and contribute to the escalating frequency of storms.
Investigation by Simon Josey and Team
Simon Josey and a team from the UK's National Oceanography Center investigated three regions that faced intense sea-ice retreat this year, using comprehensive data sources, including satellite imagery and atmospheric measurements. What they discovered was startling: areas that became ice-free experienced up to double the heat loss when compared to the more stable conditions prior to 2015.
Surge in Storm Activity
Notably, storm activity in these regions surged, with researchers noting a staggering increase in atmospheric storm frequency. In some locations, storm occurrences in June and July skyrocketed by as much as seven days per month compared to averages from 1990-2015.
Broader Climate Implications
The implications of this heat loss extend far beyond the Southern Ocean. Scientists emphasize the critical role oceans play in climate regulation and their capacity as carbon sinks, absorbing over 90% of excess heat generated by human-induced greenhouse gas emissions. The retreat of sea ice disturbs this delicate balance, raising urgent concerns about how nutrient-rich Antarctic bottom water manages heat and interacts with our global climate systems.
The Need for Urgent Action
Experts caution that if these patterns of low ice coverage persist, they may further amplify disturbances not only in the Southern Hemisphere but could also trigger far-reaching effects in the tropics and even the Northern Hemisphere.
Conclusion
The study underscores the necessity for continued investigation into the expansive climate effects of sea-ice retreat, as ignoring these changes could lead to catastrophic consequences. With the evidence mounting, the question now looms: how long do we have before we reach a tipping point? As the world watches these developments unfold, one thing remains clear: the time to act on climate change is now!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)