Shocking Discovery: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Triggered by Rare Fungal Infection - A Groundbreaking Case Study!
2024-11-21
Author: Mei
Introduction
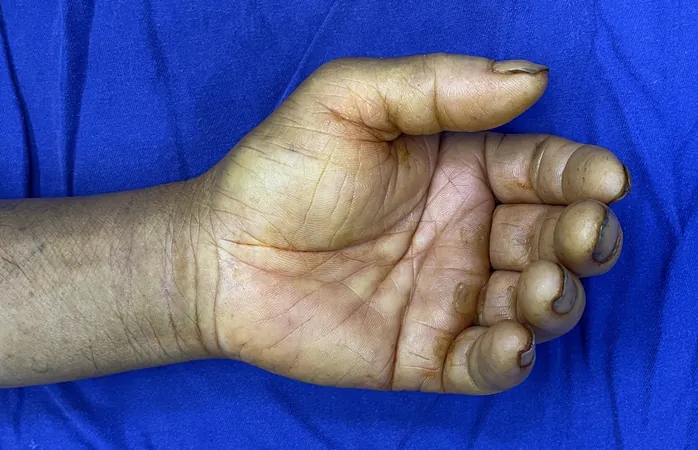
In an intriguing medical case, a patient diagnosed with carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) underwent surgical intervention for relief, which included a left carpal tunnel release and synovectomy. During the surgery, approximately 1 ml of yellow exudate was found in the carpal tunnel, with the inflamed synovium tightly adhering to the flexor tendons. Notably, the median nerve was compressed and flattened, displaying congestive changes in the epineurium.
Post-Surgery Findings and Diagnosis
Post-surgery, samples of the exudate and synovial tissue were sent for various tests, including routine bacterial and mycobacterial cultures, as well as pathology analyses. In a remarkable twist, the sequenced metagenomic samples (mNGS) conducted on the second day post-operation confirmed an infection by Arthrinium phaeospermum, a fungus previously overlooked as a potential cause for CTS.
Treatment Journey
As the situation unfolded, the patient started on rigorous antibiotic therapy with Cefoperazone and Sulbactam, but these were switched to Fluconazole when the fungal growth was identified. By the six-week postoperative follow-up, significant improvements were evident: numbness and pain in the patient's left hand were greatly alleviated, showcasing an enhanced range of motion, although some mild wrist swelling persisted.
The saga didn’t end there. Just two months post-surgery, the patient’s treatment shifted to Terbinafine. Unfortunately, this transition brought a wave of gastrointestinal distress and minimal relief from wrist swelling. Ultimately, the treatment returned to Fluconazole, leading to a steady recovery. By the six-month follow-up, there was only a trace of swelling, and after ten months, the patient achieved nearly full range of motion, reporting no symptoms at all—an exceptional turnaround!
What is Arthrinium phaeospermum?
Perhaps the most shocking element of this case is the identity of the culprit—A. phaeospermum. Initially confirmed as a pathogenic fungus by research dating back to 1980, it predominantly affects plants but poses a risk for cutaneous fungal diseases in humans and animals. Recent studies reveal its capacity to invade heads of hair follicles, leading to skin damage, primarily in immunocompromised individuals. Historically, infections caused by this fungus in human tissue have been rare, with most fungal CTS being associated with other pathogens, including typical bacteria.
Uncovering Infection-Related CTS
Carpal tunnel syndrome can be dramatically exacerbated by infections that lead to inflammation and swelling of the tissues within the carpal tunnel. This allows for compression of the median nerve, triggering typical symptoms like pain, tingling, and weakness. Notably, while infections from bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus have been well documented, the emergence of fungal infections like A. phaeospermum serves as an urgent reminder of the importance of thorough diagnostic practices.
In this case, the surgical team encountered considerable inflammation that contributed to the misdiagnosis early on, emphasizing the importance of broadening the scope of differential diagnoses when faced with atypical presentations of CTS.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)