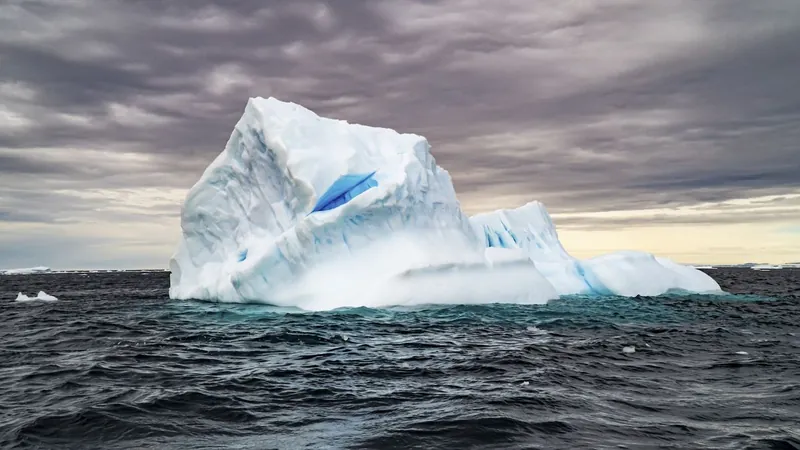

Shocking Discovery: Global Sea Levels Soared 125 Feet After the Last Ice Age!
2025-03-21
Author: Arjun
Groundbreaking Study Reveals Major Sea Level Rise
In a groundbreaking study, scientists have unveiled the astonishing truth about global sea level changes following the last ice age. Drilling beneath the surface of the North Sea, they uncovered vital geological evidence indicating that sea levels rose a staggering 125 feet (38 meters) between 11,000 and 3,000 years ago, a revelation that holds significant implications for our understanding of climate change today.
The Melting Ice Caps and Rising Sea Levels
Following the last ice age, the melting ice caps in North America, Antarctica, and Europe led to a rapid rise in sea levels as temperatures began to increase. However, until now, researchers lacked sufficient geological data to quantify the extent of this rise. This newly published study in the esteemed journal *Nature* sheds light on this monumental shift.
Research Focus on Doggerland
An international research team focused their efforts on a submerged area of the North Sea, known as “Doggerland,” which once served as a land bridge connecting the U.K. to mainland Europe until it was submerged about 7,000 years ago. The scientists extracted peat samples—evidence of ancient coastal marshlands—from beneath the sea, unraveling the history hidden in layers of sediment.
Phases of Sea Level Rise
The study reveals that the rise in sea levels occurred in two major phases. The first surge, occurring approximately 10,300 years ago, was primarily driven by the runoff from melting glaciers. The second wave of rising waters, around 8,300 years ago, was influenced by not only ice melt but also the release of significant volumes of water from glacial lakes that had formed on top of melting ice sheets.
Alarming Rate of Sea Level Rise
During this tumultuous period, sea levels climbed at an alarming rate, peaking at over 0.4 inches (10 mm) per year—a pace that is ten times the current rate of sea level rise, which stands at 0.1 to 0.2 inches (3 to 4 mm) annually. Alarmingly, projections from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) suggest that the rise could accelerate to between 0.2 and 0.4 inches (4 to 9 mm) per year by the end of this century.
The Implications for Today's Coastal Vulnerability
Sarah Bradley, a key contributor to the study and a researcher at the University of Sheffield in the U.K., emphasized the amplified risks associated with rising sea levels today. "The stakes are much higher now due to urbanization, population growth, and the presence of critical infrastructure in coastal areas. Regions that will face the brunt of climate change impacts are much more vulnerable now than they were millennia ago," she stated.
Importance of Understanding Historical Sea Level Changes
Moreover, understanding historical sea level changes helps scientists refine current climate models, enhancing our ability to predict future shifts. These paleorecords, combined with modern technological instruments, offer crucial insights into how our planet responds to unprecedented changes—knowledge that could prove essential for developing effective strategies to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
A Call to Action Against Climate Change
As the effects of climate change continue to escalate, this research highlights the urgent need for awareness and action. The past serves as both a warning and a guide, underscoring the critical importance of addressing global warming before we face even more severe consequences. What other secrets does our planet hold? The time for inquiry and action is now!
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)