Shocking Discovery: Neurons in Children with Autism Show Distinct Differences!
2024-10-09
Author: Rajesh
Shocking Discovery: Neurons in Children with Autism Show Distinct Differences!
Recent groundbreaking research has unveiled that neurons, the key communication cells in the brain, might be structurally different in children diagnosed with autism. A team of researchers at the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester has conducted an extensive study revealing significant variations in neuron density across various brain regions when comparing children with autism to their neurotypical peers.
Zachary Christensen, an MD/Ph.D. candidate at the University of Rochester School of Medicine and the lead author of a study published in the journal Autism Research, explained, “We've spent years analyzing broader characteristics of brain regions. However, advanced neuroimaging techniques are enabling us to detect remarkable complexities in brain development.”
Imaging Breakthroughs Provide New Insights on Brain Development
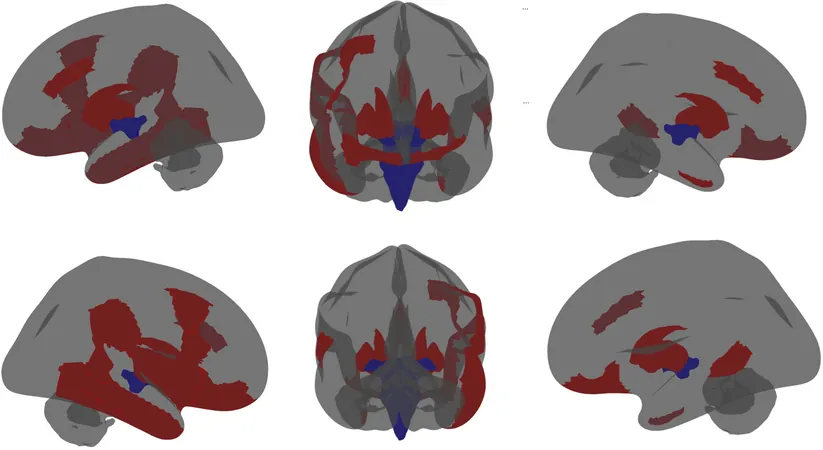
The research team utilized brain imaging data from over 11,000 children aged 9-11. By focusing on a specific group of 142 children with autism, they found a concerning pattern: a lower neuron density in several areas of the cerebral cortex—regions crucial for cognitive functions such as memory, learning, reasoning, and problem-solving. Conversely, the amygdala, an area deeply connected to emotional regulation, exhibited a higher neuron density in these children.
Notably, comparisons were also made against children diagnosed with other psychiatric disorders such as ADHD and anxiety. The results remained consistent, suggesting that these variance patterns are uniquely related to autism.
Christensen emphasized the implications of this finding: “Individuals with autism often contend with additional challenges, including anxiety and depression. However, this research gives us a new framework to understand autism's unique characteristics, potentially guiding more tailored therapeutic interventions moving forward.”
Harnessing Technology for Enhanced Understanding of Autism and Brain Function
The technological advancements utilized in this study have significantly improved the precision with which researchers can examine neuronal structures—something previously achievable only through postmortem analyses. The brain imaging data were sourced from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study, the largest ongoing investigation into brain development and child health, initiated in 2015. This remarkable study has dramatically transformed our knowledge regarding adolescent brain health and developmental processes.
John Foxe, Ph.D., and senior author of the study, remarked, “We're just beginning to comprehend the transformative implications of the ABCD Study data. As we continue to follow these children into early adulthood, our understanding of brain development is set to evolve dramatically.”
The future holds great promise as this research paves the way for more personalized approaches to autism diagnosis and treatment. Stay tuned for more breakthroughs in brain research that could change lives!





 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)