Shocking Discovery: New Species of Pangolin Unveiled Amidst Trafficking Crisis!
2025-01-09
Author: Rajesh
Groundbreaking Discovery
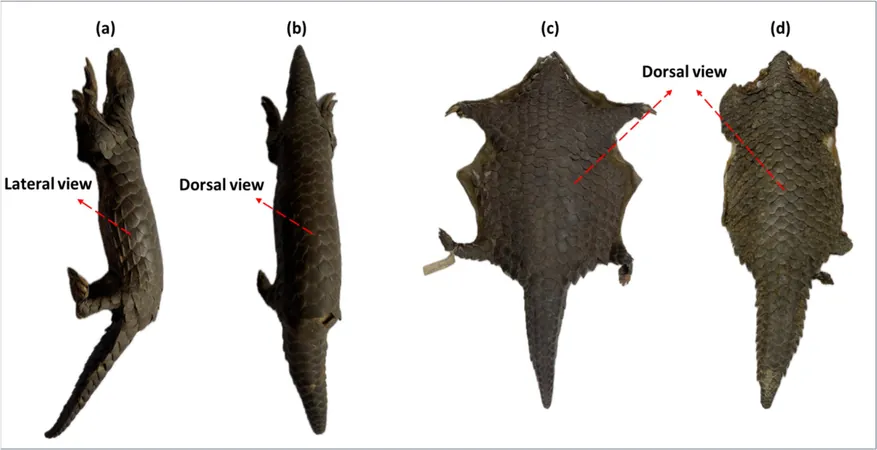
In a groundbreaking revelation, scientists from the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) in Kolkata have identified a brand-new species of Asian pangolin while analyzing DNA from confiscated pangolins. This newly recognized creature has been proposed to be named the Indo-Burmese pangolin (Manis indoburmanica). These remarkable animals, often likened to scaly anteaters, possess a distinct appearance and play an essential role in maintaining ecological balance.
Unique Adaptations
Did you know? Pangolins are the only mammals covered in hard, protective keratin scales. This unique adaptation allows them to curl into a ball when threatened, serving as a natural armor against predators. With eight different species of pangolins—four located in Africa and four in Asia—these enigmatic creatures primarily consume ants and termites, using their long, sticky tongues to capture their prey.
Conservation Crisis
The plight of the pangolin is alarming; they rank amongst the most trafficked mammals in the world, primarily due to high demand for their scales in traditional medicine and as luxury products. These fascinating creatures also serve as indicators of environmental health, making their conservation imperative. Their survival can reveal the state of the ecosystem, providing invaluable insights to researchers focused on environmental monitoring.
Genetic Research
In this recent research initiative, a team of scientists delved into the genetic diversity of Asian pangolins through mitochondrial DNA analysis—a powerful tool for studying evolutionary relationships. By examining the DNA of 41 individual pangolins, including newly sequenced samples, the researchers unearthed a hidden lineage that diverged from the Chinese pangolin nearly 3.4 million years ago during the Pliocene Epoch.
Species Classification
To corroborate the classification of the Indo-Burmese pangolin as a distinct species, the researchers conducted a series of analyses. By measuring genetic distance using metrics like the Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery (ABGD) method, they found that the genetic differences between the Indo-Burmese pangolins and their closest relatives, the Chinese pangolins, were substantial enough to warrant new species classification. A barcode gap of 3.8% further confirmed these differences.
Phylogenetic Analysis
Furthermore, by employing the entire mitochondrial genome to construct a phylogenetic tree, the scientists visually cemented the Indo-Burmese pangolin's unique position within the pangolin family tree. This breakthrough emphasizes the need for urgent conservation actions.
Geological Influences
But what led to the formation of this new species? The researchers hypothesize that significant geological and climatic shifts during the Pliocene and Pleistocene epochs, particularly the rise of the Tibetan Plateau, played a substantial role. These changes fostered isolated habitats, allowing unique evolutionary paths to flourish, resulting in the emergence of the Indo-Burmese pangolin.
Future Research and Conservation
While this discovery is indeed a monumental leap forward for science, there is still much work to be done. Further studies are crucial to unravel the intricacies of the Indo-Burmese pangolin's habitat, diet, and the threats it faces, including poaching and habitat loss. For the pangolin's survival, it is essential that innovative conservation strategies, bolstered by research like this, are implemented to safeguard these incredible animals from the brink of extinction.
Conclusion
Stay tuned as the world watches what steps are taken next to protect these extraordinary creatures!
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)