
Shocking Findings: Obesity Costs the US Industry Over $347 Billion Annually!
2024-12-06
Author: Wei
Introduction
A groundbreaking study featured in *Nature Nutrition & Diabetes* has revealed that the staggering economic impact of obesity on the US industry exceeds $347 billion in 2023. This research paints a vivid picture of the repercussions of obesity among American workers, highlighting an urgent call to action for both businesses and policymakers.
Study Overview
Published on December 4, 2024, the study scrutinized health and economic data from national surveys involving 158 million employees across seven key industries in the United States. By examining the relationship between body weight and workplace productivity, the researchers found that a modest weight loss of just 5% to 25% could lead to remarkable medical savings—estimated between $153.3 billion and $326.1 billion over five years!
Financial Impact
The financial toll is staggering: the authors uncovered that each obese employee imposes an average annual cost of $6,472 on their employer, while those classified as overweight contribute an average of $1,244. The primary culprits driving these costs include excessive medical expenses, productivity losses, absenteeism, and disability payments. The authors emphasized that these findings "highlight the need for resources dedicated to treatment and prevention," which could substantially lower medical expenditures and enhance overall productivity in the workforce.
Market Dynamics
This research was conducted by a team of analysts at GlobalData, the parent organization of Pharmaceutical Technology, revealing critical insights at a time when the obesity crisis is intensifying. The significance of these findings aligns closely with the recent surge in the obesity medication market, particularly focusing on glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1-RAs) manufactured by industry leaders such as Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly.
Revenue Growth
Despite a slight dip in overall industry revenues in 2023, GlobalData reports that these leading firms are experiencing phenomenal growth, with Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly achieving revenue increases of 31.3% and 19.6%, respectively.
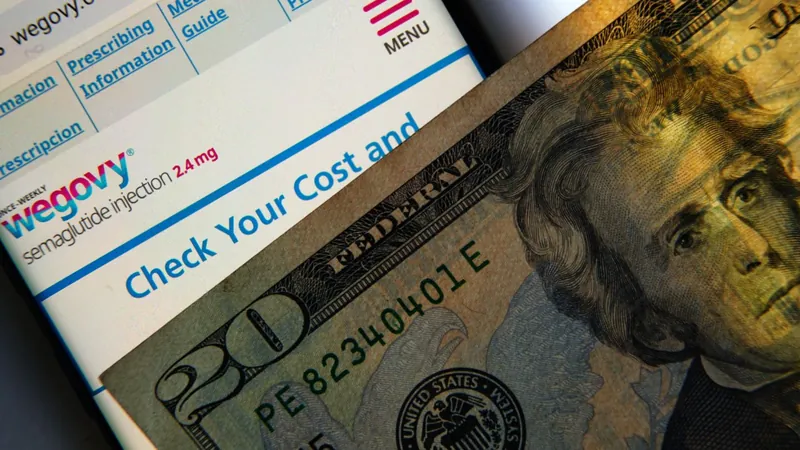
Leading Products
Among the front-runners in this market are Novo Nordisk's groundbreaking drugs, Ozempic and Wegovy (semaglutide), projected to generate an astonishing $17.8 billion and $8.4 billion in global revenues for 2024. Meanwhile, Lilly's formidable contenders, Mounjaro and Zepbound (tirzepatide), are anticipated to bring in $11.8 billion and $5.4 billion, respectively.
Zepbound's Success
Notably, Zepbound has recently outperformed Wegovy, demonstrating 47% greater weight loss in Phase III trials, raising new hopes for obesity management.
Market Predictions
As the anti-obesity market is set to soar to an estimated $30 billion by 2030 across major global markets—including France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, the UK, and the US—other biopharmaceutical companies like AstraZeneca, Amgen, and Roche are also exploring innovative metabolic therapies.
Emerging Alternatives
The demand for oral GLP-1RAs as potential alternatives to the current injectable options is escalating, with Phase III candidates like Rybelsus and NN-9932 from Novo Nordisk, as well as orforglipron from Lilly, nearing approval.
Policy Developments
In a significant move, the Biden administration recently proposed expanding Medicare and Medicaid access to GLP-1RAs for individuals with obesity alone, potentially benefiting over 42% of the US population and opening the floodgates for more widespread treatment options.
UK Regulations
However, not all aspects of this emerging landscape are positive. The UK government has announced plans to restrict access to Mounjaro starting next year, which is intended for individuals with a body mass index (BMI) above 35—impacting approximately 3.4 million people across the adult population.
Conclusion
With obesity emerging as a formidable challenge to public health and economic stability, this new study underscores the critical need for comprehensive strategies aimed at prevention and treatment, as the nation grapples with the far-reaching consequences of this epidemic. The question remains: will the US take decisive action before the crisis escalates further?

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)