Shocking Findings: Peptic Ulcer Disease Leads to Spike in Hospitalizations and Deaths!
2025-01-09
Author: Siti
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a pressing health issue, connected with an alarming increase in hospitalizations and mortality rates, as highlighted by a comprehensive review published in JAMA. While proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) have emerged as the standard go-to treatment, addressing underlying causes, such as Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infections and the discontinuation of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), is crucial for preventing recurrence.
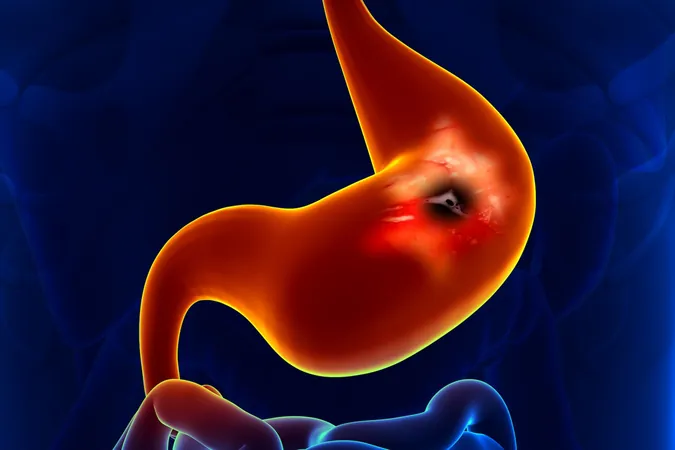
What exactly is a peptic ulcer?
It's essentially a painful sore formed in the lining of the stomach, the lower esophagus, or the upper part of the small intestine, known as the duodenum. In the United States, the prevalence of this disease stands at about 103 cases per 100,000 individuals, with an annual incidence of 44 per 100,000. On a global scale, the rates differ widely, often influenced by regional H. pylori infection prevalence and patterns of NSAID consumption.
Eye-Opening Statistics About Global Ulcer Disease
Understanding the gravity of the situation, a recent study in BMC Gastroenterology revealed a staggering 25.8% rise in the global prevalence of peptic ulcer disease from 1990 to 2019, with numbers continuing to surge. While mortality rates have indeed decreased significantly over the past three decades, this paradox underscores an urgent need for more research into the factors influencing these trends.
Peptic ulcer disease affects an estimated 5% to 10% of the global population during their lifetime. Researchers combed through literature from 2000 to 2024, analyzing clinical trials and observational studies to better grasp the factors contributing to the rise of ulcer disease.
Common Causes of Peptic Ulcer Disease
The investigation revealed some striking insights into the common risk factors for PUD. Approximately 41.8% of individuals with peptic ulcer disease are affected by H. pylori infections, while around 36.1% are linked to NSAID or aspirin use, and 22.1% have no identifiable cause.
The golden standard for diagnosis? An endoscopy. This procedure allows healthcare providers to visualize ulcers directly, assess bleeding, and check for H. pylori infection. The sensitivity of endoscopy outstrips double-contrast barium tests significantly, making it an invaluable tool for accurate diagnosis. Experts suggest that anyone diagnosed with peptic ulcer disease should also be tested for H. pylori as part of their treatment regimen.
Effective Treatment Strategies to Combat PUD
The findings emphasize a three-pronged strategy to alleviate the burden of peptic ulcer disease. First, the primary treatment focuses on acid inhibition to facilitate the healing of existing ulcers. Second, PPIs play a crucial role in eradicating H. pylori infections, thereby reducing overall acidity and working synergistically with antibiotics. Lastly, managing lifestyle factors such as tobacco use and the prudent use of NSAIDs are essential in preventing the recurrence of ulcers.
The study concluded that the link between peptic ulcer disease, increased hospitalizations, and mortality cannot be ignored. PPIs, like omeprazole and lansoprazole, stand out as the first line of defense against ulcers, but eliminating H. pylori and controlling NSAID use are indispensable steps to curb recurrence.
The Takeaway: Empower Yourself with Knowledge
As peptic ulcer disease continues to pose serious health threats globally, it is essential for individuals to stay informed about symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options. Don't let ignorance leave you vulnerable – educate yourself and your loved ones about this condition.
The battle against peptic ulcer disease is far from over, and we must unite in our efforts to raise awareness, improve prevention measures, and enhance treatment strategies. In this way, we can work towards a future where peptic ulcers are not the silent killers they are today.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)