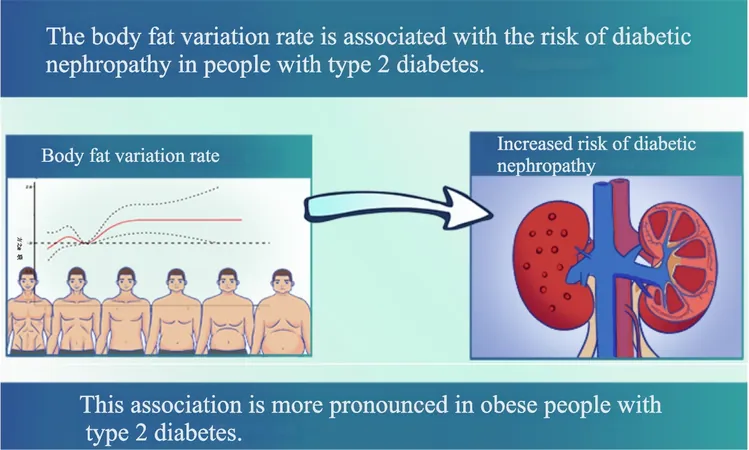
Shocking New Findings Reveal Link Between Body Fat Fluctuations and Diabetic Nephropathy Risk!
2024-10-14
Author: Sarah
Introduction
As the global crisis of diabetes escalates, with projections estimating that roughly 592 million people will be affected by 2035, understanding the nuances of diabetes management becomes crucial. Recent research has surfaced, shedding light on the relationship between body fat variation and the risk of developing diabetic nephropathy (DN) among individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM). But what does this mean for diabetes patients seeking effective weight loss strategies?
Background and Purpose of Study
In diabetes management, weight control is often viewed as a pivotal strategy to stave off complications like diabetic nephropathy—a condition characterized by progressive kidney damage and one of diabetes' most serious complications. Yet, there was a glaring gap in understanding how fluctuations in body fat during weight loss programs impact this risk. This study explored the link between the rate of body fat variation and the incidence of diabetic nephropathy in American patients with T2DM.
Methodology Overview
Using the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) database, researchers calculated body fat variation rates over two years. This extensive, randomized clinical trial incorporated data from over 10,000 participants, but researchers focused on 4,609 individuals, analyzing risk factors and health outcomes related to body fat levels.
Participants were divided into two distinct groups based on their body fat variation rates over the study period, allowing for a clear examination of trends and outcomes. Statistical analyses included hazard ratio estimations and Cox proportional hazards models to comprehend the potential implications of body fat fluctuation on DN risk, particularly focusing on how body mass index (BMI) interacted with these changes.
Key Findings
In a striking revelation, those with higher rates of body fat variation faced an increased risk of developing diabetic nephropathy, with those exhibiting the most considerable fluctuations being 1.13 times more likely to develop the condition compared to those with stable body fat levels. Notably, this correlation was particularly pronounced in participants classified as obese (BMI > 30), with the risk soaring to 1.34 times.
This study also unveiled critical insights regarding body fat variation relative to individuals’ BMI classifications, revealing that drastic fluctuations posed higher risks primarily to obese patients, emphasizing the need for tailored weight loss strategies that minimize volatility in body composition.
The Implications of Body Composition Management
The implications of these findings are profound. They suggest that adopting gradual weight loss strategies may be paramount for obese individuals with diabetes. Rather than chasing quick fixes, a consistent and moderate approach to weight management could better aid in protecting kidney function over time.
Furthermore, the study hints at overarching systemic issues. The patterns of body fat fluctuation appear to stimulate inflammatory responses, which may have cascading effects on microvascular complications of diabetes, bridging the knowledge gap about obesity's contributing role in diabetic complications.
Recommendations for Diabetes Patients
Given these revelations, healthcare providers should consider personalized weight loss strategies that promote gradual changes in body fat. Additionally, awareness of body fat variation rates and their implications on nephropathy risk should become a standard conversation between diabetes patients and their healthcare teams.
Conclusion: A Call for Further Research
The findings are groundbreaking, paving the way for future research aimed at exploring the mechanisms behind body fat variation and its impact on diabetic nephropathy risk more comprehensively. While obesity continues to be a critical determinant in diabetes management, understanding how fluctuations in body fat percentages influence health outcomes could usher in new guidelines for effective diabetes care.
As the field of diabetes research evolves, staying informed and advocating for healthy, sustainable approaches will be vital for individuals living with this chronic condition. Keep an eye on this space as we continue to uncover more about the profound connections between body composition and diabetes outcomes!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)