Shocking New Study Unlocks Secrets of Bed Bug Genomes: Experts Reveal Resistance Mutations That Make Them Invincible!
2024-12-17
Author: Rajesh
Breakthrough in Genome Mapping
Scientists have achieved a landmark breakthrough by mapping nearly flawless genomes of both susceptible and highly resistant bed bug strains, revealing why these pesky pests remain resilient despite our best efforts to eradicate them. The shocking findings were published in the esteemed journal "Insects," shedding light on the genetic adaptations that have allowed bed bugs to bounce back in alarming numbers over the past two decades.
Historically, bed bugs (Cimex lectularius) were nearly eliminated by the 1960s, thanks to widespread application of insecticides like DDT. However, the resurgence of these blood-sucking insects can be attributed to resistance mutations that developed against these chemicals amidst evolving pest control practices.
Resistance isn't just a mere inconvenience; it poses significant health risks as while bed bugs do not transmit diseases, their bites can lead to severe skin irritations and secondary infections. This newly published research highlights two main resistance mechanisms: metabolic resistance, where bed bugs produce enzymes that detoxify insecticides, and penetration resistance, which involves developing thicker cuticles to prevent insecticide absorption.
Genome Sequencing Breakthrough: A Jigsaw Puzzle Like No Other!
Led by Hidemasa Bono, a professor at Hiroshima University's Graduate School of Integrated Sciences for Life, the research team meticulously sequenced the genomes of both susceptible strains—descendants of wild populations collected 68 years ago—and superresistant strains bred from bed bugs found in a Hiroshima hotel in 2010. The resistant specimens showcased an astonishing 19,859-fold increase in resistance to pyrethroids, the primary weapon used in bed bug management.
The process of genomic mapping can be likened to assembling a mammoth jigsaw puzzle. Unlike traditional sequencing methods which cover only small snippets of DNA leading to gaps, the innovative long-read sequencing method used in this study allowed researchers to piece together a more complete picture of the genomes. With an impressive completeness of 97.8% for the susceptible strain and 94.9% for the resistant strain, these genomes surpassed previous reference standards in terms of quality and comprehensiveness.
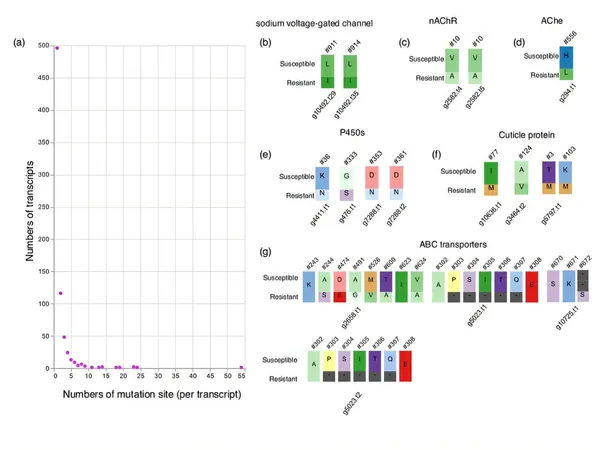
What makes these findings even more extraordinary is the identification of nearly 4,000 transcripts with amino acid mismatches; notably, 729 of these were tied to insecticide resistance. Kouhei Toga, the study’s lead author, emphasized the importance of these discoveries, stating, "By comparing amino acid sequences, we can pinpoint specific mutations that confer resistance, potentially unlocking new strategies for pest control."
New Discoveries Fuel Future Pest Control Tactics
This groundbreaking research also unearthed several previously unknown mutations that could redefine how we approach bed bug management. Researchers identified genes involved in critical biological processes, such as DNA damage response and insulin metabolism, suggesting that these pathways may play a crucial role in enhancing resistance to pyrethroids.
"By editing these genes, we can gain invaluable insights into the evolution and mechanisms of insecticide resistance among bed bugs," added Toga. This opens up avenues for developing more effective pest control measures with a stronger focus on genetic factors influencing resistance.
As the bed bug crisis continues to escalate globally, this study highlights the urgent need for innovative genomic research in order to develop smarter, more efficient pest management strategies. The implications of these findings could shape the future of tackling one of humanity's most persistent foes—bed bugs.
Stay tuned for updates, as this research lays the foundation for potential breakthroughs that may finally put an end to these unyielding intruders in our homes!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)