Shocking Revelation: Your Energy Comes Solely from Mom! Here’s Why It Matters.
2024-10-09
Author: Arjun
Introduction
For ages, we’ve known that our DNA is a blend of both parents, but a groundbreaking new study reveals a stunning twist: we inherit our mitochondrial DNA, responsible for powering our cells, exclusively from our mothers! This phenomenon has puzzled scientists for eons, with dads’ contributions effectively erased the moment the sperm meets the egg.
A New Dawn for Understanding Mitochondrial Disorders
Conducted using the model organism C. elegans, roundworms that share many biological features with humans, the research shines a light on mitochondrial disorders—conditions that affect the body's energy production and impact an estimated 1 in 5,000 individuals. These disorders remain poorly understood, but there’s a flicker of hope on the horizon: vitamin K2, known for its benefits in bone health, might play a role in preventing or treating these conditions.
Senior author Ding Xue, a professor at CU Boulder, stated, 'These findings provide crucial insights into the necessity of eliminating paternal mitochondria early on in development. They also open up new avenues for treating mitochondrial diseases that could arise when this mechanism is disrupted.'
The Science of Energy Production
Mitochondria serve as tiny powerhouses within our cells, generating adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency essential for virtually all cellular functions. While they do possess their DNA, the exclusive maternal inheritance raises questions about evolutionary advantages—and the study suggests that paternal mitochondria might be genetically compromised after their tough journey to the egg.
Xue previously published pioneering work on how paternal mitochondria are eliminated through a self-destruct process called paternal mitochondria elimination (PME). This mechanism, which operates across various species, might explain why evolutionary biology favors maternal mitochondrial inheritance.
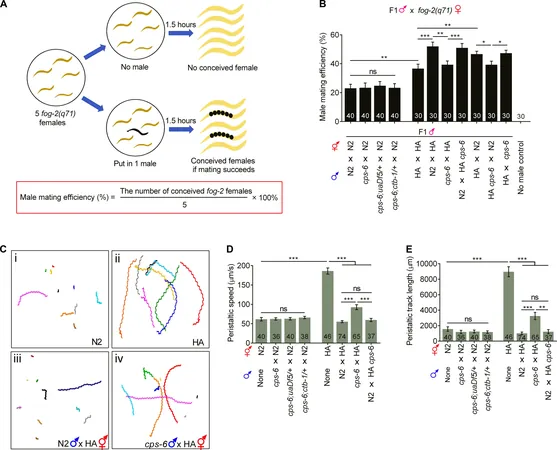
During their research, Xue and his team found that when they inhibited PME in C. elegans, it significantly affected ATP production in fertilized eggs. The result? Worms suffered from cognitive impairments, reduced physical activity, and reproductive challenges.
In a twist of fate, treatment with MK-4, a form of vitamin K2, restored ATP levels to normal and revitalized memory and reproductive functions in these worms—potentially providing a beacon of hope for human applications.
A Practical Path Forward for Families
Though only a handful of cases exist where paternal mitochondrial DNA has been confirmed in humans, the implications of this research can't be understated. Xue speculates that the same mechanisms observed in worms might also apply to human mitochondrial diseases, which often remain mysterious and challenging to diagnose.
Imagine a future where families at risk for mitochondrial disorders could take vitamin K2 as a precautionary measure during pregnancy! This research could pave the path toward innovative diagnostic tools and treatment strategies that empower individuals to combat mitochondrial diseases.
As Xue concludes, 'ATP problems can influence every aspect of human life. With this study, we are taking the first steps toward unraveling the mysteries of mitochondrial dysfunction—a journey that could change lives.'
Conclusion
Get ready to rethink everything you knew about your energy sources—because the secrets locked within your mother’s DNA could unlock groundbreaking health advancements for generations to come!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)