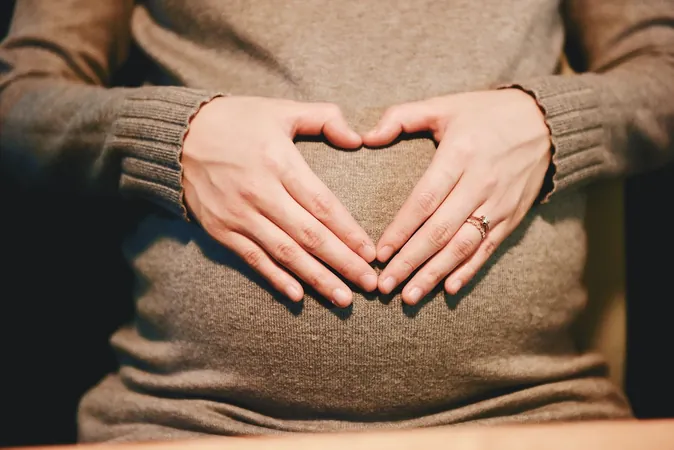

Shocking Study Reveals Link Between Prediabetes in Youth and Pregnancy Complications – What Every Parent Needs to Know!
2024-09-24
The Rising Tide of Prediabetes Among Youth
Prediabetes is a serious health issue characterized by elevated blood sugar levels that are not high enough to be classified as type 2 diabetes. This condition is particularly alarming as it can increase the likelihood of heart disease and stroke, with a disproportionate impact on Hispanic, Black, and low-income populations. According to reports from JAMA Pediatrics, the rate of prediabetes among U.S. youth has skyrocketed over the last decade, now affecting nearly one in three individuals aged 12 to 19.
An Eye-Opening Investigation
The Mount Sinai research team conducted a retrospective cohort study involving over 14,000 participants aged 10 to 24 by integrating data from New York City's birth registry, hospital discharge records, and the A1C Registry between 2009 and 2017. All subjects had no prior diabetes history and had undergone at least one hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test before their first birth.
The findings were striking: young women with prediabetes faced over double the risk of developing gestational diabetes during their first pregnancy. Furthermore, the study demonstrated that prediabetes in young adults could lead to an 18% higher likelihood of experiencing hypertensive disorders during pregnancy, including gestational hypertension and preeclampsia, as well as an increased risk of preterm deliveries.
Critical Screening Recommendations
Researchers identified that the optimal hemoglobin A1c threshold for adolescents was slightly lower than that for adults (5.6% compared to 5.7%), indicating the necessity for tailored screening specific to younger populations. "The lack of uniform preconception prediabetes treatment guidelines for adolescents may represent a missed opportunity to avert pregnancy-related complications," noted Dr. Katharine McCarthy, the study's lead author and Assistant Professor at the Icahn School of Medicine.
The research further emphasizes the urgent need for clinical guidelines that address how to effectively screen and counsel adolescents with elevated blood sugar levels without additional risk factors. This innovation could serve as a vital intervention strategy, tackling cardiometabolic risks at an early stage in life.
Looking Ahead: Interventions for a Healthier Future
The research team is now seeking to explore potential school policies and intervention strategies designed to mitigate risks associated with heart and metabolic disorders during adolescence. These initiatives could play a crucial role in enhancing not only pregnancy outcomes but also overall health across a person’s lifespan.
With the alarming rise of prediabetes among young people, it’s more important than ever for families to become informed about the signs and risks associated with this condition. Preventive strategies could be key to ensuring healthier generations to come.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)