Shocking Study Reveals Parkinson's Drug Dangers: Are Your Gut Bacteria at Risk?
2024-11-21
Author: Jia
A groundbreaking new study has unveiled that entacapone, a widely prescribed medication for Parkinson's disease, may wreak havoc on the gut microbiome by causing iron deficiency. This alarming discovery emphasizes the often-overlooked consequences of human-targeted drugs on our vital microbial communities, which are essential for overall health.
The research, conducted by an international team including experts from the University of Vienna, the University of Southampton, Aalborg University, and Boston University, was published in Nature Microbiology and falls under the framework of the Cluster of Excellence "Microbiomes drive Planetary Health." It highlights that while antibiotics are notorious for disrupting gut microbiota, many other medications—especially those aimed at neurological disorders—also have significant adverse effects on these microbial populations.
Traditionally, studies exploring drug-microbiome interactions have either relied on patient cohort analyses influenced by numerous confounding factors or focused on isolated gut bacteria, a method that fails to capture the intricate complexity of the human microbiome.
A Revolutionary Approach to Understanding Drug Effects
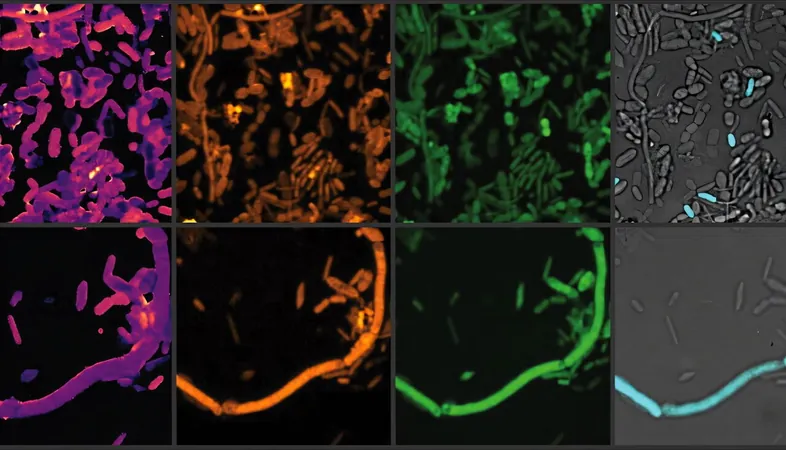
In this innovative study, researchers deployed a unique experimental design to assess the impact of entacapone and loxapine (a schizophrenia medication) on fecal samples from healthy donors. By incubating these samples with therapeutic doses of the two drugs and employing advanced techniques such as heavy water labeling and Stimulated Raman Spectroscopy (SRS), they revealed startling impacts on microbial health.
The results were striking; not only did entacapone and loxapine severely inhibit many gut bacteria, but they also caused a dramatic increase in E. coli populations, particularly in the presence of entacapone. Lead author Fatima Pereira pointed out, "Using the heavy water-SRS method allowed us to detect nuanced changes in the gut microbiome that traditional methods often overlook."
Iron Deficiency: The Silent Saboteur
The study found that entacapone induces iron starvation in the gut, a critical nutrient for many bacterial species. The researchers were able to mitigate the drug's detrimental effects by supplementing fecal samples with iron, which counteracted the imbalances caused by entacapone. Notably, it was discovered that E. coli exploited an effective iron-uptake system to thrive even in low-iron conditions, highlighting a new mechanism of drug-induced gut dysbiosis that promotes the growth of potentially harmful microbes.
"This research uncovers how entacapone contributes to gut dysbiosis by favoring E. coli and similar pathogens under iron-limiting conditions," stated Michael Wagner, scientific director of the Excellence Cluster.
Implications for Patients and Future Treatments
The ramifications of these findings stretch far beyond Parkinson's treatment. With many human-targeted medications containing metal-binding structures, it’s plausible that similar mechanisms of microbiome alteration could be widespread. The study opens the door for improved therapeutic strategies, potentially allowing for modifications in drug administration to better protect the gut microbiome.
Wagner emphasized, "Our next move is to investigate how we can adjust drug therapies to support gut health, possibly by providing a targeted iron delivery system that benefits microbiota without hindering drug absorption."
As researchers continue to unravel the complexities of gut-health interactions with medications, patients taking drugs like entacapone may soon have options to mitigate side effects linked to gut dysbiosis. This pivotal study serves as a wake-up call, urging further investigation into how our medicines might be unintentionally harming our internal ecosystems. Could the solution to better health lie not just in medication, but in how we understand and support the gut microbiome? Stay tuned for developments that could reshape treatment protocols in the quest for holistic health!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)