Significant Changes in Oral Microbiota Linked to Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease in Children – What Parents Must Know!
2024-11-21
Author: Rajesh
Introduction
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD), a common childhood illness caused primarily by enterovirus A 71 (EV-A71), has raised concerns among parents worldwide due to its potential complications and prevalence. Emerging research indicates that this viral infection not only affects physical health but also contributes to alterations in the oral microbiome, which plays a crucial role in children’s overall well-being.
Study Overview
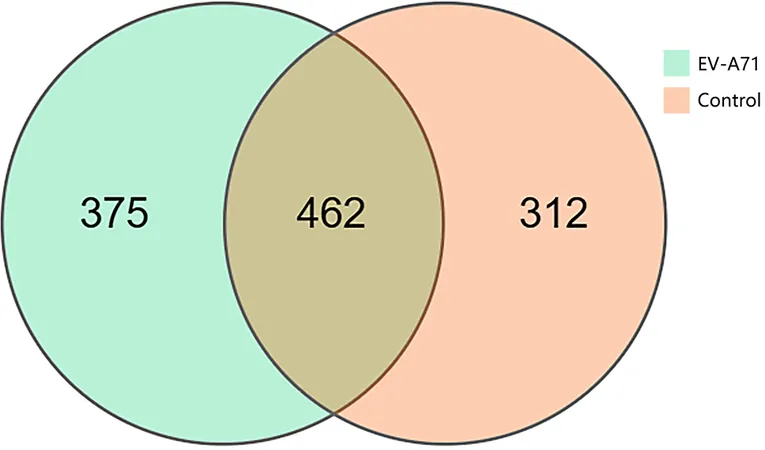
A recent study analyzed the oral microbiota of 80 children diagnosed with HFMD due to EV-A71, alongside 30 healthy controls, from April 2021 to September 2023. By utilizing the advanced 16 S rRNA gene sequencing technology, researchers sought to uncover structural changes in the oral microbiota associated with this viral infection.
Key Findings
The findings revealed significant differences in the oral microbiota between the EV-A71 group and the healthy controls. Notably, children with HFMD exhibited:
- **Reduced Microbial Diversity**: The Shannon Diversity Index and Abundance-Based Coverage Estimator (ACE) index both indicated a marked decline in microbial diversity among children with HFMD compared to healthy peers.
- **Specific Bacterial Changes**: The prevalence of critical genera like Capnocytophaga and Leptotrichia was significantly lower in the HFMD group, which has implications for oral health and immune response.
The Bigger Picture: Why Oral Microbiota Matters
The oral microbiota is vital for maintaining oral health and preventing infections. Disruption of its balance can lead to inflammation and increased susceptibility to other infections. This research reinforces the understanding that the microbiome not only reflects health status but also actively influences the progression of diseases, including HFMD.
What Parents Should Be Aware Of
Given the clinical implications observed in this study, parents should consider:
1. **Monitoring Oral Health**: Regular dental check-ups can help in assessing and maintaining the oral microbiome, especially during viral infections like HFMD.
2. **Probiotic Benefits**: Introducing probiotics may help restore balance to the oral microbiota. Research suggests that enhancing the diversity of beneficial bacteria can alleviate symptoms associated with oral lesions often seen in HFMD.
3. **Staying Informed**: Awareness of potential complications of HFMD, such as neurological impacts, is crucial. Understanding the link between oral health and systemic diseases can guide preventive measures.
Conclusion
The ongoing crisis of HFMD demands more than just symptomatic treatment; it necessitates a comprehensive approach encompassing oral microbiota health. Further investigation is essential to elucidate the exact mechanisms behind these changes and to explore effective interventions. By prioritizing oral health, we can support the overall well-being of children, particularly those at risk from infections like EV-A71.
With these insights, parents can better safeguard their children, providing a healthier future amidst rising concerns over viral infections.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)