The Hidden Dangers of Helicobacter Pylori: A Surprising Link to Cardiovascular Disease Revealed!
2024-12-18
Author: Arjun
Background
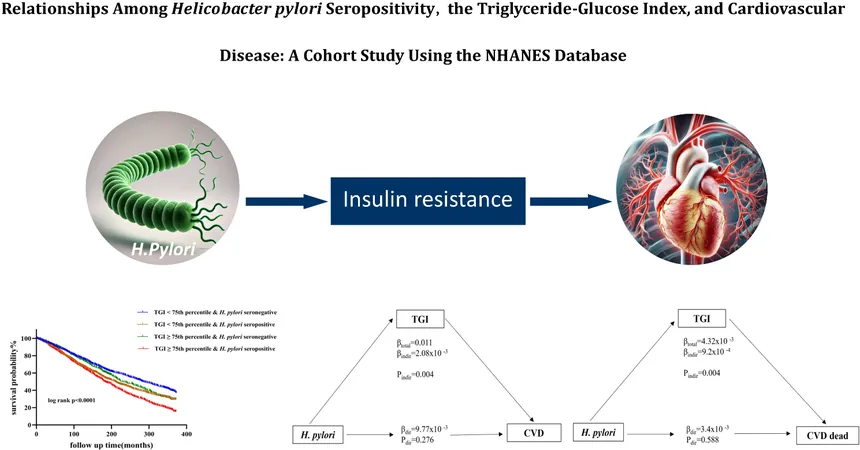
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), a common digestive tract bacterium that can easily be treated, is emerging as a potential factor influencing the risk of cardiovascular diseases (CVD). While treatment for H. pylori is simple, its relationship with heart-related ailments continues to spark debate among scientists and health professionals alike. This study delves into how the triglyceride-glucose index (TGI), a crucial marker for insulin resistance, may shape this complex relationship.
Research Methods
Utilizing extensive data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) collected between 1988 and 2000, this study scrutinizes how H. pylori seropositivity, TGI levels, and cardiovascular health intertwine. Statistical models—including logistic regression and Cox proportional hazards models—were employed to determine the impact of these factors on CVD and all-cause mortality (ACM).
Key Findings
Out of 9,399 individuals, nearly half (47.75%) tested positive for H. pylori antibodies, and 41.86% had been diagnosed with CVD. Alarmingly, those with a TGI in the highest bracket and positive H. pylori results were found to have a significantly elevated risk for CVD, supporting an odds ratio of 1.487. Additionally, ACM risk soared to a hazard ratio of 1.227 among CVD patients concurrently exhibiting high TGI and H. pylori infection.
Intriguingly, the study revealed that H. pylori may indirectly enhance CVD and mortality risk through the TGI. This suggests that by monitoring both H. pylori serological status and TGI levels, healthcare providers could significantly bolster their capacity to predict and manage cardiovascular risks.
Implications and Future Directions
These findings underscore the critical need for routine screening for H. pylori among patients with cardiovascular diseases. Eradicating this pathogen could be transformational in reducing cardiovascular risk and improving patient outcomes. Medical professionals are urged to consider integrating H. pylori serology tests as part of overall assessments for heart health.
Concluding Thoughts
With the implications of H. pylori seropositivity potentially leading to increased cardiovascular risks, public health campaigns focused on H. pylori awareness and eradication could pave the way for healthier communities. However, further prospective studies are essential to definitively establish the protective benefits of H. pylori eradication against CVD.
Call to Action: Could Your Gut Health Impact Your Heart?
This study prompts an urgent question: Is your TGI level and H. pylori status putting your cardiovascular health at risk? Stay informed and consult with your healthcare provider about screening options today!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)