The Hidden Threat of Dormant Food Pathogens: A Game Changer for Consumer Safety?
2024-10-02
The Hidden Threat of Dormant Food Pathogens: A Game Changer for Consumer Safety?
In a remarkable breakthrough, scientists from INRAE and the esteemed Institut Pasteur have unveiled the enigmatic behavior of Listeria monocytogenes, the harmful bacterium responsible for listeriosis, a potentially fatal infection. This organism has the unsettling ability to enter a dormant state when exposed to unfavorable conditions, such as disinfectants or nutrient-poor environments, making it nearly invisible to standard detection methods used in the food industry and hospitals.
We're diving deep into how this discovery alters the landscape of food safety and public health risk management. According to a recent article published in *Nature Communications*, the traditional methods for detecting pathogens rely heavily on cultivating live bacteria from a sample. Unfortunately, this approach fails to reveal the presence of bacteria that have gone dormant—a state known as "viable but non-culturable" (VBNC). These dormant pathogens can reactivate under favorable conditions, turning into active threats again.
Listeria monocytogenes lurks in various environments, from soil and rivers to plants, and can lead to listeriosis, which boasts a deadly mortality rate of up to 30% for vulnerable populations, including the elderly and pregnant women. Although this bacterium has previously demonstrated the ability to enter VBNC states in controlled environments, the nuances of how it does so were not fully understood—until now.
Unlocking the Mechanism of Dormancy
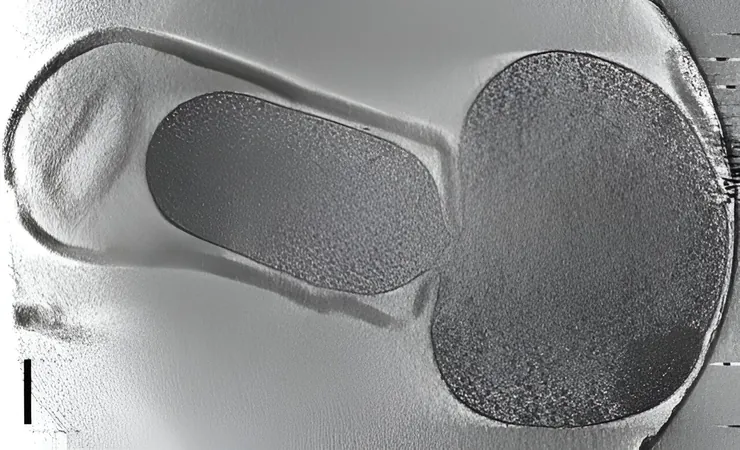
Researchers subjected Listeria monocytogenes to mineral spring water, simulating a low-nutrient environment. Astonishingly, they found that during the shift to the VBNC state, the bacteria undergo a dramatic transformation. They lose their characteristic rod shape, morphing into a rounded form as they shed their protective cell wall, a structure crucial for maintaining their shape and integrity.
Even without a cell wall, these dormant bacteria show remarkable resilience, adjusting their membranes and producing specific proteins to adapt to harsh conditions. To combat this hidden threat, scientists have devised targeted antibodies that can detect these dormant forms of Listeria, a development set to revolutionize detection strategies.
The Public Health Implications
These findings not only highlight an underappreciated aspect of bacterial survival but also emphasize the critical role of bacterial cell structure in the emergence of such dormant states. The ability of Listeria monocytogenes to form undetectable reservoirs raises alarming public health concerns. If these bacteria can frequently adapt and become untraceable, public safety in food consumption could be at greater risk than previously understood.
The researchers are not stopping there. They aim to delve deeper into the factors influencing the dormant state and the conditions that could trigger a comeback to virulence. By creating precise detection tools, they hope to mitigate the risks associated with this cunning pathogen.
The Urgent Call for Enhanced Food Safety Measures
As the implications of this research unfold, it becomes more crucial than ever for food safety protocols to evolve. With the potential for previously undetectable pathogens to reappear, the food industry and healthcare services must adopt cutting-edge detection techniques. Could this be the key to ensuring safer food consumption and preventing outbreaks of listeriosis? Stay tuned as we watch this thrilling narrative of science and public safety develop. Your health could depend on it!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)