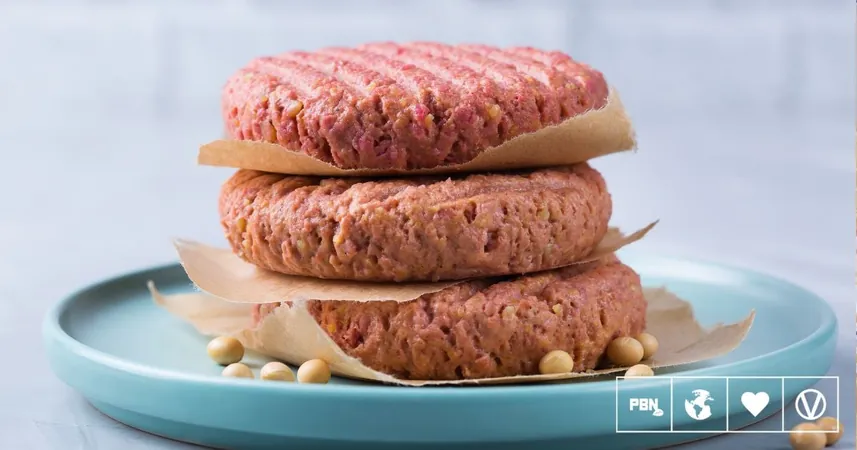

The Surprising Health Benefits of Plant-Based Alternatives Over Animal Products
2024-11-27
Author: Daniel
Recent research from ProVeg International reveals that plant-based meat and milk options can be as nutritious, if not more so, than their animal-derived equivalents. This groundbreaking report examined the nutritional profiles of 422 plant-based meat alternatives and 251 plant-based milk options from 11 different countries, providing a comprehensive comparison to animal-based products in line with global nutrition guidelines, such as those from the World Health Organization (WHO) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA).
Key Findings: Nutritional Superiority
The findings indicate that plant milks generally contain lower total fat and saturated fat levels than conventional cow’s milk. Notably, soy milk stood out as the healthiest plant-based option, providing a protein content comparable to that of cow's milk. Adding to the health argument, a recent study suggests that consuming soy milk can lead to reductions in blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and inflammation, even in its sweetened form.
Moreover, the analysis found that plant-based meats offered a significant reduction in saturated fat while boasting far more dietary fiber than their animal-based counterparts. This fiber boost is essential for digestive health and can aid in weight management, making it a favorable choice for conscious consumers.
The Importance of Fortification
Fortification played a vital role in the nutritional quality of plant-based products. The report highlighted that certain fortified plant-based options surpassed the nutritional profiles of animal-derived products. However, the degree of fortification varied notably among nations. For instance, most plant milks were fortified with calcium—averaging 120 mg per 100 ml—matching the calcium content found in cow’s milk. Notably, countries like the UK and the US also fortified these products with additional nutrients such as vitamin D and B12, although practices vary widely.
In the realm of plant-based meats, fortification is still a budding practice, with the Netherlands leading the way—more than 70% of their plant-based meat products are fortified with iron and B12. In contrast, other regions have not yet implemented similar standards consistently.
Tackling Salt and Sugar Content
Interestingly, while the average salt content in plant-based meats reached 1.3 grams per 100 grams—exceeding the healthy limit—it still remained lower than the average 1.1 grams found in similar animal products. On the sugar front, while some plant-based milks do contain added sugars, all reviewed options were notably less sugary than traditional cow’s milk, which contains naturally occurring lactose.
Recommendations for a Healthier Future
The report makes several actionable recommendations tailored for various stakeholders, from producers to consumers. Food manufacturers are urged to develop healthier formulations that minimize harmful ingredients like excess salt while enhancing nutritional content through fortification.
Governments have a role to play as well. By establishing national guidelines, they can help elevate the health standards of plant-based alternatives. From a consumer perspective, it is essential to choose products that are lower in added sugars, saturated fats, and salt.
Anna-Lena Klapp, the report's co-author and Head of Research at ProVeg, emphasizes the potential of plant-based alternatives: “This report underscores how varied plant-based options can diversify diets and replace the dominant animal-based products on the market. These alternatives can bridge the gap between current eating habits and healthier, sustainable diets. Collaboration across sectors will be key in promoting better dietary choices.”
Conclusion
As the world shifts towards more sustainable eating practices, the evidence mounts that plant-based alternatives not only provide a viable substitute for animal products, but also deliver significant health benefits. With further advancements in fortification and education, these products could become staple items on shelves worldwide, paving the way for a healthier planet and population.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)