
Unbelievable Discovery: Hidden Ecosystem Revealed as Giant Iceberg Splinters from Antarctica!
2025-04-04
Author: Arjun
In an extraordinary turn of events, a team of international researchers has uncovered a stunning aquatic ecosystem previously shrouded beneath the icy embrace of Antarctica. This revelation came shortly after a colossal iceberg, named A-84 and comparable in size to the city of Chicago, broke away from the George VI Ice Shelf in the Bellingshausen Sea on January 13, 2025.
The momentous calving of this iceberg unveiled an expansive 209 square miles (540 square kilometers) of previously concealed seafloor, yielding a unique opportunity for scientists. On January 25, the research team aboard the Schmidt Ocean Institute’s R/V Falkor (too) eagerly descended into these uncharted waters for the first large-scale study of the underwater environment that had been hidden for centuries.
A Thriving Underwater Sanctuary: New Discoveries Await!
The expedition took an unexpected turn as researchers adjusted their original plans to capitalize on this once-in-a-lifetime opportunity. Co-chief scientist Patricia Esquete from Portugal's University of Aveiro remarked, “We didn’t anticipate uncovering such a vibrant ecosystem,” noting that the observed communities of marine life may have thrived unnoticed for decades or even centuries.
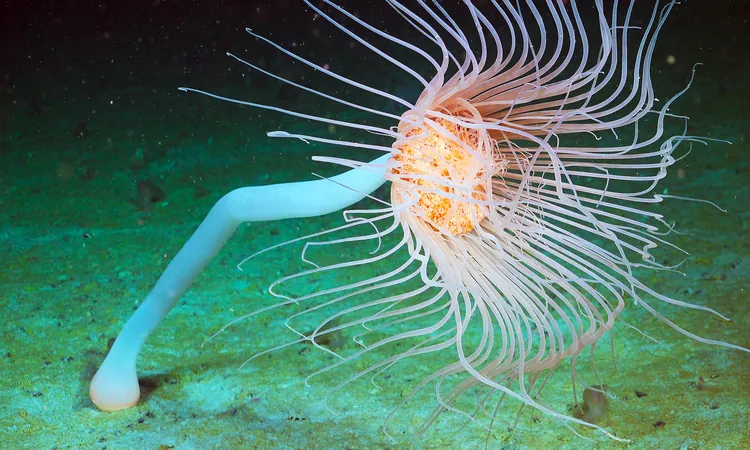
Utilizing the Schmidt Ocean Institute’s remotely operated vehicle, ROV SuBastian, the team spent eight days exploring depths of up to 1,300 meters (4,265 feet). Their findings were nothing short of astonishing; they encountered a rich mix of corals, sponges, icefish, giant sea spiders, and octopuses—an indication that life can flourish even under regions once dominated by vast ice sheets.
Interestingly, prior studies, such as those conducted by researchers from the British Antarctic Survey in 2021, hinted at possible marine life beneath the ice, but this mission marked the first comprehensive documentation of such diverse and plentiful ecosystems.
How Life Thrives in Total Darkness?
The researchers speculate on how this vibrant life survives in an environment devoid of sunlight. Typically, deep-sea ecosystems rely on nutrients that drift down from above, yet these ecosystems remained buried under nearly 500 feet of ice for centuries. Scientists are investigating how ocean currents may be delivering essential nutrients to support these remarkable communities.
Implications for Climate Change Research
Beyond ecological exploration, the team is also analyzing geological samples to understand the historical behaviors of the Antarctic ice sheet. In light of climate change, the accelerating loss of this massive ice cover adds urgency to these studies, as it significantly contributes to rising sea levels globally.
Co-chief scientist Sasha Montelli of University College London stressed the importance of this mission: “Understanding these changes provides critical context for predicting future impacts and shaping effective conservation policies.”
The Bigger Picture: A Global Initiative
This groundbreaking expedition is part of the Challenger 150 initiative, a global collaborative effort aiming to advance knowledge of deep-sea biology, recognized by the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO for its significance.
Jyotika Virmani, executive director of the Schmidt Ocean Institute, emphasized the serendipitous nature of this discovery, stating, “Being present at such a pivotal moment allows us to witness the untouched beauty of our world and the hidden marvels within.”
As the researchers continue their analysis, their findings hold significant implications regarding the adaptability of marine species and the resilience of Antarctic habitats, highlighting the pressing necessity for enhanced global conservation efforts.
Keep an eye out for updates regarding this unprecedented discovery, as researchers delve deeper into understanding the complexities of the Antarctic ecosystems!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)